城市濕地建設(shè)的戰(zhàn)略性途徑:自然保護(hù)、工程與景觀設(shè)計(jì)的融合
Strategic Approaches to Urban Wetlands: Reconciling Nature Conservation, Engineering and Landscape Architecture
作者:安琪?施托克曼�����、約翰內(nèi)斯?約爾格 Author: Antje STOKMAN, Johannes J?RG
摘要 ……
濕地是世界上最具生產(chǎn)力�,同時(shí)也是最為瀕危的生態(tài)系統(tǒng)之一。城市化是濕地面臨的一項(xiàng)主要威脅��。在城市環(huán)境中�,與濕地相伴而生的是與水相關(guān)的疾病、洪水��、污染以及惡劣的生活環(huán)境�����,這樣的狀況已持續(xù)了相當(dāng)長(zhǎng)的一段時(shí)間�����。
自20世紀(jì)末���,人們對(duì)待濕地的態(tài)度發(fā)生了根本性的轉(zhuǎn)變:《拉姆薩爾濕地公約》的提出強(qiáng)調(diào)了濕地在自然保護(hù)方面的諸多積極的價(jià)值�����,并且推動(dòng)了濕地管理新概念的產(chǎn)生以消減其健康隱患���。同時(shí)�,工程學(xué)大力倡導(dǎo)人工濕地和生物過(guò)濾池能夠有效地吸收并凈化來(lái)自雨洪徑流����、廢水,以及受污河流中的污染物這一理念�����。景觀設(shè)計(jì)將具有審美與娛樂(lè)價(jià)值的城市濕地公園與生態(tài)和技術(shù)要素整合在一起����,發(fā)展出了更為出色的理念���,展示出在城市環(huán)境中���,濕地恢復(fù)與建造這一綜合性的戰(zhàn)略途徑所具有的巨大潛力��。本文呈現(xiàn)了有關(guān)城市濕地的不同觀點(diǎn)��,并且對(duì)相應(yīng)的案例如何在城市生態(tài)系統(tǒng)中發(fā)揮重要作用進(jìn)行了討論����。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
整合設(shè)計(jì)����;景觀基礎(chǔ)設(shè)施;生態(tài)系統(tǒng)績(jī)效��;生態(tài)工程�����;人工濕地����;水資源綜合管理
Abstract ...
Wetlands are at the same time among the most productive and the most threatened ecosystems of the world. One of the major threats for wetlands is urbanization. In the urban context there is a long history of associating wetlands with a number of water-related diseases, floods, pollution and poor living conditions.
Since the end of the 20th century, there has been a paradigm shift in the attitude towards wetlands: the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands has promoted the importance of new concepts of wetland management in order to reduce health hazards by highlighting the many positive wetland values from the perspective of nature conservation. At the same time, engineering has broadly introduced the concept of constructed wetlands and biofilters as a way of effectively trapping and removing the pollution from stormwater run-off, wastewater and polluted river water. Linking the ecological and technical dimensions and integrating them with the high aesthetic and recreational value of urban wetland parks, landscape architecture has developed fascinating concepts demonstrating the high potential of an integrated strategic approach to the recovery and creation of wetlands in the urban context. This paper brings together these different perspectives on urban wetlands and argues by discussing different case-studies how wetlands can take a prominent role in urban ecosystems.
Key words ...
Integrated Design; Landscape Infrastructure; Ecosystem Performance; Ecological Engineering; Constructed Wetland; Integrated Water Management
景觀績(jī)效:濕地治理系統(tǒng)和自然化景觀的量化效益與經(jīng)驗(yàn)總結(jié)
Landscape Performance: Quantified Benefits and Lessons Learned from a Treatment Wetland System and Naturalized Landscapes
作者:李明翰、布魯斯?德沃夏克�����、羅毅、馬特?鮑姆加登 Author: Ming-Han LI, Bruce DVORAK, Yi LUO, Matt BAUMGARTEN
摘要 ……
根據(jù)景觀設(shè)計(jì)基金會(huì)的定義��,景觀績(jī)效是一項(xiàng)“衡量景觀解決方案在實(shí)現(xiàn)其預(yù)設(shè)目標(biāo)的同時(shí)滿足可持續(xù)性方面的效率的指標(biāo)”�����。景觀績(jī)效在近些年成為了一個(gè)非常熱門(mén)的研究焦點(diǎn)�,其理論框架建立在可持續(xù)性的三元體系之上:環(huán)境、經(jīng)濟(jì)和社會(huì)��。建成景觀設(shè)施的績(jī)效可通過(guò)其環(huán)境�����、經(jīng)濟(jì)和社會(huì)效益的量化結(jié)果得到體現(xiàn)��。本文記述了一項(xiàng)對(duì)一個(gè)范圍約1 300hm2�����、采用了濕地治理系統(tǒng)和自然化景觀的總體規(guī)劃性社區(qū)所進(jìn)行的景觀績(jī)效調(diào)查����,并對(duì)其中的經(jīng)驗(yàn)進(jìn)行了總結(jié)。研究團(tuán)隊(duì)確定了環(huán)境��、經(jīng)濟(jì)和社會(huì)衡量標(biāo)準(zhǔn)���,收集了能夠反映出該系統(tǒng)績(jī)效成果的數(shù)據(jù)��,并對(duì)水質(zhì)���、土壤肥力和草本植物多樣性進(jìn)行了調(diào)查。此外�����,研究團(tuán)隊(duì)還對(duì)潛在和實(shí)際利益進(jìn)行了量化�,包括固碳,以及通過(guò)減少草坪修剪��、肥料施用和用于灌溉的飲用水而節(jié)省成本���。文中對(duì)環(huán)境����、經(jīng)濟(jì)和社會(huì)方面的效益成果進(jìn)行了討論����,并對(duì)建設(shè)過(guò)程中和建成之后各個(gè)階段的管理和維護(hù)事項(xiàng)的相關(guān)經(jīng)驗(yàn)進(jìn)行了總結(jié)。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
雨洪;水質(zhì)�����;景觀維護(hù)����;草原;景觀感知
Abstract ...
Landscape performance, as defined by the Landscape Architecture Foundation, is “the measure of efficiency with which landscape solutions fulfill their intended purpose and contribute toward sustainability.” It is becoming a popular research focus in recent years; and its theoretical framework is built upon the sustainability triad: environment, economy and society. Through the quantification of environmental, economic and social benefits of a built landscape, its performance can be determined. This paper presents results from a landscape performance investigation and the lessons learned from a 3,200-acre master planned community that employs a treatment wetland system and naturalized landscapes. The research team identified environmental, economic and social metrics, and then collected data that reveals the performance results of the installed systems. Water quality, soil fertility, and herbaceous plant diversity were investigated. In addition, the research team quantified potential and actual benefits, including sequestration of carbon dioxide, and cost savings through the use of reduced mowing, fertilizer use, and reduction of irrigation with potable water. Environmental, economic and social benefit results are discussed. Lessons learned from management and maintenance issues during and post construction phases are summarized.
Key words ...
Stormwater; Water Quality; Landscape Maintenance; Prairie; Landscape Perception
土壤:水系統(tǒng)中被忽視的向度
Soil: The Unseen Layer of Water
作者:張志維 Author: Chih-Wei G. V. CHANG
摘要 ……
健康的土壤在水文中扮演著調(diào)節(jié)水量與控制水質(zhì)的重要角色����,對(duì)于水與土之間相互影響的忽視,往往是造成水系統(tǒng)設(shè)計(jì)失敗的原因���。例如�����,土壤過(guò)度夯實(shí)或結(jié)構(gòu)遭到破壞�,會(huì)在雨洪管理中影響土壤的滲透率與保水力�����,因而增加地表徑流��;土壤中有機(jī)質(zhì)的流失,會(huì)降低土壤的凈水效能����,破壞營(yíng)養(yǎng)物質(zhì)與沉積物�,從而導(dǎo)致水污染。為了將土壤知識(shí)納入景觀設(shè)計(jì)工作中�,本文建議在設(shè)計(jì)過(guò)程中增加土壤管理專(zhuān)項(xiàng)。其中與水系統(tǒng)相關(guān)的最佳實(shí)踐包括:1)保護(hù)既有的土壤以保持原有水文�����;2)避免及改善土壤夯實(shí)以增加保水率����;3)保存及重建土壤有機(jī)質(zhì)以改善水質(zhì)。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
健康土壤�;土壤夯實(shí);土壤有機(jī)質(zhì)流失��;雨洪管理��;土壤保護(hù)��;土壤管理
Abstract ...
Healthy soil performs important functions in regulating water volume and controlling water quality. However, overlooking such dynamics between soil and water often leads to design misassumption and water system failure. For instance, the compacted soil and disturbed soil profile result in poor water retaining capacity and increased surface runoff. The organic matter loss decrease soil’s effectiveness at binding and breaking down nutrients and sediments, which further pollute the water system. To incorporate soil sciences in design and construction processes, implementing a soil management plan is suggested. The best soil practices for water system includes 1) Protecting soil structure to conserve hydrological performance; 2) Avoiding and amending soil compaction to increase water retaining capacity; 3) Conserving and restoring soil performance in water cleansing.
Key words ...
Healthy Soil; Soil Compaction; Soil Organic Loss; Stormwater Management; Soil Conservation; Soil Management
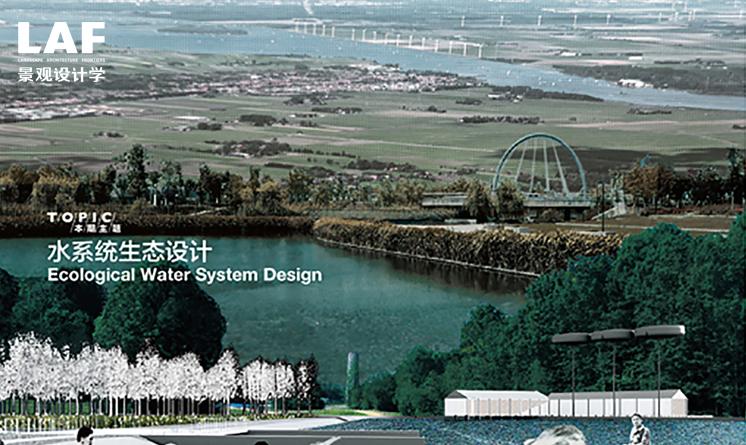
基于自然過(guò)程的人工干預(yù)下的水系統(tǒng)生態(tài)設(shè)計(jì)
Ecological Water System Design under Human Intervention Based on Natural Processes
作者:鄭曦 Author: Xi ZHENG
摘要 ……
水系統(tǒng)生態(tài)設(shè)計(jì)是一種利用人工干預(yù)的方式��,介入自然過(guò)程、調(diào)節(jié)人居環(huán)境的工程化的生態(tài)處理方式����。本文探討了水系統(tǒng)生態(tài)設(shè)計(jì)的內(nèi)涵、不同尺度的水系統(tǒng)之間的關(guān)聯(lián)�����,并結(jié)合具體項(xiàng)目說(shuō)明如何進(jìn)行水系統(tǒng)生態(tài)設(shè)計(jì)與建設(shè)���,以及古代理水理念對(duì)于當(dāng)代水系統(tǒng)生態(tài)設(shè)計(jì)的借鑒意義�。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
水系統(tǒng)���;生態(tài)設(shè)計(jì)���;人工干預(yù);古代理水理念
Abstract ...
Ecological water system design is an approach to ecological engineering that intervenes natural processes and regulates the living environment through human intervention. This article discusses the scope of ecological water system design and the relationships between water systems at different scales. Citing several built projects, this paper illustrates how to construct ecological water systems, while also analyzing the instructive significance of ancient water management to current methods of ecological water system design.
Key words ...
Water System; Ecological Design; Human Intervention; Ancient Water Management Concept
人性化的城市雨水景觀設(shè)計(jì)對(duì)策
People-oriented Design Solutions in Urban Rainwater Landscapes
作者:孫鵬�����、王志芳�����、姜芊孜、王華清 Author: Peng SUN, Zhifang WANG, Qianzi JIANG, Huaqing WANG
摘要 ……
城市雨洪綜合利用的根本目的在于促進(jìn)地方水文的良性循環(huán)�����,解決地方水問(wèn)題����。城市是人類(lèi)活動(dòng)的集中地區(qū)�����,城市中的大多數(shù)工程設(shè)施都無(wú)可避免地要考慮人的使用需求����,然而這一點(diǎn)卻常常為傳統(tǒng)的工程設(shè)計(jì)所忽視。本文提出了兩種人性化的城市雨洪綜合利用對(duì)策—彈性對(duì)策以及防御對(duì)策���,并歸納總結(jié)了針對(duì)不同策略的設(shè)計(jì)手法�,以期進(jìn)一步促進(jìn)雨洪綜合利用在城市中的推廣����,從而構(gòu)建城市中的“人水和諧”。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
人類(lèi)活動(dòng)��;景觀設(shè)計(jì);城市水文���;雨洪利用
Abstract ...
The fundamental purpose of the comprehensive utilization of urban stormwater is to improve the cycle of local hydrology, and respond to local water issues. Most of urban engineering facilities cannot avoid considering human uses and needs, because a city is a concentrated area of human activities. However, this point is often overlooked by the traditional design in engineering. In this paper, two people-oriented design strategies of comprehensive stormwater utilization are proposed: adaptive strategy and protective strategy. Moreover, it summarizes the design solutions for different strategies to further promote the comprehensive stormwater utilization in cities to establish a harmonious relationship between human and water.
Key words ...
Human Activities; Landscape Design; Urban Hydrology; Stormwater Utilization
關(guān)于中國(guó)“風(fēng)景園林學(xué)”的5個(gè)問(wèn)題
Five Questions about Landscape Architecture in China
作者:楊銳 Author: Rui YANG
摘要 ……
本文從“風(fēng)景園林學(xué)”的學(xué)科名稱(chēng)展開(kāi)�����,分別就5個(gè)問(wèn)題進(jìn)行了討論:在新一輪的國(guó)家學(xué)科調(diào)整中����,為何會(huì)將“風(fēng)景園林學(xué)”定為一級(jí)學(xué)科的名稱(chēng)�?“學(xué)科”的概念以及建設(shè)“風(fēng)景園林學(xué)術(shù)共同體”的重要性?風(fēng)景園林學(xué)的前景如何��?中國(guó)的風(fēng)景園林學(xué)所要解決的關(guān)鍵問(wèn)題是什么��?以及當(dāng)代中國(guó)需要怎樣的風(fēng)景園林學(xué)�?
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
風(fēng)景園林學(xué);學(xué)科發(fā)展����;名稱(chēng);風(fēng)景園林共同體��;當(dāng)代中國(guó)
Abstract ...
Using the discipline name of “Landscape Architecture” as a framework, this article addresses five questions: Why did “Feng Jing Yuan Lin Xue (風(fēng)景園林學(xué))” become the Chinese name for the discipline of landscape architecture during the national disciplinary adjustment? What is the concept of “Discipline” and the significance of “Landscape Architecture Academic Community”? What is the future trajectory of landscape architecture in China? What are the key issues that need to be addressed by landscape architecture in China? And what kind of landscape architecture does contemporary China need?
Key words ...
Landscape Architecture; Discipline Development; Name; Landscape Architecture Academic Community; Contemporary China
跨尺度的城市水系生態(tài)設(shè)計(jì):昆明滇池水系綠道
Ecologies for an Urban River System across Scales: Dianchi Greenways in Kunming
作者:俞孔堅(jiān)�����、孫鵬、賈軍 Author: Kongjian YU, Peng SUN, Jun JIA
摘要 ……
本項(xiàng)目對(duì)昆明滇池治理問(wèn)題提出了系統(tǒng)的解決方案��,通過(guò)建構(gòu)生態(tài)安全格局����,將35條流入滇池的河流作為水生態(tài)凈化系統(tǒng)和過(guò)濾器。整合雨洪利用系統(tǒng)�、生物棲息地網(wǎng)絡(luò)、文化遺產(chǎn)網(wǎng)絡(luò)����,以及自行車(chē)和步行綠道���,構(gòu)成一個(gè)綜合解決城市水環(huán)境問(wèn)題的生態(tài)基礎(chǔ)設(shè)施�����。項(xiàng)目對(duì)綠道系統(tǒng)周邊的土地利用進(jìn)行調(diào)整��,力求通過(guò)解決河流生態(tài)恢復(fù)�����、兩岸雨污治理���、提高土地利用綜合效益��、增強(qiáng)河流吸引力等問(wèn)題���,實(shí)現(xiàn)生態(tài)效益、社會(huì)效益和經(jīng)濟(jì)效益的最大化����,還昆明以寧?kù)o、美麗�����、健康和充滿活力的母親河��。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
生態(tài)安全格局����;跨尺度設(shè)計(jì);生態(tài)恢復(fù)����;雨洪管理
Abstract ...
The project launches a systematic planning for the Dianchi Lake pollution treatment. An ecological security pattern is set up and 35 rivers flowing into Dianchi Lake are taken as ecological water purification system and filters. The stormwater collection system, bio-habitant network, cultural heritage and greenways for bicycles and pedestrians are integrated as an ecological infrastructure to solve urban water environment problems in a comprehensive way. It adjusts the land use surrounding the greenway system, and attempts to maximize the benefit of ecology, citizens and economics through river ecological restoration, rain sewage management, improvement of land use efficiency. Finally, Panlong River, the mother river of Kunming, would be revitalized to be peaceful, beautiful, healthy and active.
Key words ...
Ecological Security Pattern; Cross-scale Design; Ecological Restoration; Stormwater Management
基于現(xiàn)實(shí)的生態(tài)建設(shè)—杭州“西溪里”項(xiàng)目景觀設(shè)計(jì)與思考
Building an Environmental Friendly Community— Design and Review on Xixi Village in Hangzhou
作者:盛梅 Author: Mei SHENG
摘要 ……
本項(xiàng)目是一個(gè)在綜合雨水管理指導(dǎo)下完成的景觀設(shè)計(jì)作品��,通過(guò)雨水工程師與景觀設(shè)計(jì)師的合作����,室外空間與生態(tài)雨水系統(tǒng)形成充分融合����、相互依存的關(guān)系,使環(huán)境的生態(tài)可持續(xù)性和品質(zhì)得以保證��。同時(shí)��,通過(guò)在項(xiàng)目實(shí)施中暴露出的矛盾���,本文對(duì)景觀設(shè)計(jì)行業(yè)發(fā)展中一些尚待解決的問(wèn)題進(jìn)行了討論。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
綜合雨水管理�����;可持續(xù)設(shè)計(jì)����;政府規(guī)范;綠色基礎(chǔ)設(shè)施;專(zhuān)業(yè)銜接�����;專(zhuān)業(yè)教育
Abstract ...
The design of Xixi Village is a project guided by the Low Impact Development principles. Through collaborations between landscape architects and engineers, an integrated stormwater system has been created within a community’s outdoor space and water features, providing a showcase of environment-friendly development. Through the process of this project, issues of collaboration between architects, landscape architects and engineers were exposed and addressed. Longstanding practices of stormwater management must be challenged to assure sustainable development that would reduce flooding, improve water quality and enhance overall living quality.
Key words ...
Stormwater Management; Sustainable Design; Government Regulations; Green Infrastructure; Inter-disciplinary Collaboration; Professional Education
蕪湖商務(wù)文化中心中央公園
Central Park of the Central Commercial and Cultural District, Wuhu
作者:奧雅設(shè)計(jì)集團(tuán) Author: L&A Design Group
摘要 ……
該項(xiàng)目位于蕪湖商務(wù)文化中心�,為占地48hm2的帶狀城市公共綠地。景觀規(guī)劃運(yùn)用了“河����、道、丘�����、林”四大要素���,打造出一條“山水間的綠飄帶”�,并結(jié)合周邊城市功能��,布置了林蔭山地園��、雕塑園等8個(gè)主題園區(qū)��。為了保證公園的生態(tài)功能�����,項(xiàng)目采用一系列如石籠駁岸與生態(tài)草溝等低成本的環(huán)保設(shè)計(jì)元素,彰顯出“可持續(xù)發(fā)展”的生態(tài)設(shè)計(jì)理念�����。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
中央公園�����;主題園���;生態(tài)���;河道
Abstract ...
The recent construction of the Wuhu commercial and cultural district created a dynamic commercial space while also establishing an ecologically functional landscape nestled within a high-density urban area. Using a series of low-cost methods such as stone gabions, bioswales, and native planting, the design successfully turned 3.2 kilometers of undeveloped land with poor soil and consistent flooding into an active and popular urban park, providing a vegetative leisure space for the local community.
Key words ...
Central Park; Theme Park; Ecology; Waterway
荷蘭費(fèi)爾森市維克格公園
Wijkeroogpark in Velsen, the Netherlands
作者:Bureau B+B城市規(guī)劃與景觀設(shè)計(jì)事務(wù)所 Author: Bureau B+B Urban Design and Landscape Architecture
摘要 ……
古老的斯奇比克河在維克格公園中得到了重現(xiàn),與公園延伸空間中新建的步行道和自行車(chē)道相互呼應(yīng)�����。河流時(shí)隱時(shí)現(xiàn)����,仿佛在和游客們捉迷藏���。精心設(shè)計(jì)的混凝土河堤和自然式河岸勾勒出溪流的輪廓���。淡水流入大壩底部盛滿北海半咸水的池塘中���。這一淡咸水的交換過(guò)程所產(chǎn)生的特殊鹽度為喜半咸水環(huán)境的動(dòng)植物的生長(zhǎng)創(chuàng)造了絕佳的棲息地。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
公園���;水�����;融匯���;植物群落;動(dòng)物群落
Abstract ...
The old brook Scheybeek is made visible in the park. The brook has been staged together with the new pedestrian and bicycle paths in the extended spaces in the park. A game of meeting and disappearing takes place between the visitor and the stream. The stream’s profile is composed from a specially designed concrete element and a natural embankment. The sweet brook water flows out into a pond of brackish North Sea water at the bottom of the dike. The unique salinity originating from this exchange of water is the perfect place for flora and fauna specific to brackish water.
Key words ...
Park; Water; Encounters; Flora; Fauna
荷蘭阿姆斯福特市法特霍斯特社區(qū)總體規(guī)劃
Master Plan for Vathorst in Amersfoort, the Netherlands
作者:West 8城市規(guī)劃與景觀設(shè)計(jì)事務(wù)所 Author: West 8 urban design & landscape architecture b.v.
摘要 ……
在荷蘭阿姆斯福特市法特霍斯特社區(qū)的總體規(guī)劃中���,高柏伙伴規(guī)劃園林和建筑事務(wù)所及West 8城市規(guī)劃與景觀設(shè)計(jì)事務(wù)所強(qiáng)調(diào)景觀并非城市發(fā)展的附加物或美化手段����,而應(yīng)被看作是獨(dú)立的實(shí)體和規(guī)劃中充滿活力的組成部分�����。該總體規(guī)劃依照荷蘭傳統(tǒng)運(yùn)河城市的形式進(jìn)行設(shè)計(jì),通過(guò)水路而非公路進(jìn)行組織����,使得法特霍斯特社區(qū)成為了一座生機(jī)勃勃的水城。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
社區(qū)�;運(yùn)河;水之城���;生態(tài)改善
Abstract ...
The master plan for Vathorst in Amersfoort, the Netherlands, was developed by Kuiper Compagnons and West 8, highlights that the landscape is not an afterthought or a beautifier to urban development, but is considered a vital entity in itself and an active component of the plan.The master plan was designed in the tradition of old Dutch canal cities, using waterways as organizing elements rather than roadways, allowing Vathorst to be an active water city.
Key words ...
Community; Canal; Water City; Ecological Improvement
荷蘭鹿特丹市班特布雷水廣場(chǎng)
Water Square Benthemplein in Rotterdam, the Netherlands
作者:DE URBANISTEN城市研究和設(shè)計(jì)工作室 Author: DE URBANISTEN
摘要 ……
作為一項(xiàng)創(chuàng)新的雙重戰(zhàn)略�����,班特布雷水廣場(chǎng)將城市蓄水與城市公共空間質(zhì)量的提升結(jié)合起來(lái)����。廣場(chǎng)在平時(shí)保持旱景狀態(tài)并作為年輕人運(yùn)動(dòng)和玩耍的空間���;當(dāng)遭遇強(qiáng)降雨時(shí)�,廣場(chǎng)將一改往常的外觀和功能���,“變身”為一個(gè)臨時(shí)的雨水儲(chǔ)存設(shè)施�����。三個(gè)下沉廣場(chǎng)被用來(lái)收集雨水:兩個(gè)較淺的廣場(chǎng)在平時(shí)能夠迅速收集廣場(chǎng)周邊的雨水��;一個(gè)較深的廣場(chǎng)只有在遭受連續(xù)降雨時(shí)才會(huì)啟動(dòng)雨水收集功能��。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
水廣場(chǎng)��;參與式設(shè)計(jì)�;雨水儲(chǔ)存設(shè)施��;不銹鋼水槽
Abstract ...
The design of Water Square Benthemplein is an innovative twofold strategy that combines water storage and improves the quality of urban public space. Most of the time the square is dry and used as a recreational space for youth sports and play. When confronted with heavy rainfall, the square changes from its usual appearance and function, becoming a temporary rainwater storage facility. Three basins were designed to collect rainwater: two undeep basins will receive water for the immediate surroundings and one deeper basin will only receive water when it is consistently raining.
Key words ...
Water Square; Participatory Design; Rainwater Storage Facility; Stainless Steel Gutter
林中物流:描繪瓦爾登湖及其全球本土化資源傳遞
Logistics in the Woods: Mapping Walden and its Glocal Resource Relays
作者:梅格?斯杜德 Author: Meg STUDER
摘要 ……
盡管近來(lái)景觀都市主義將關(guān)注點(diǎn)放在農(nóng)業(yè)烏托邦以及分散聚落策略方面����,但梭羅的《瓦爾登湖》,或稱(chēng)《林中生活散記》���,這部經(jīng)典的環(huán)境保護(hù)主義著作����,仍然被解讀為關(guān)于自我審視的田園生活經(jīng)歷��。筆者目前的項(xiàng)目—“邊緣運(yùn)作”或稱(chēng)“林中物流”�����,則對(duì)《瓦爾登湖》進(jìn)行了“量化分析”?���!斑吘夁\(yùn)作”研究透過(guò)梭羅的“城郊”視角,關(guān)注由瓦爾登湖向外擴(kuò)展的一系列過(guò)程—從林地到壁爐���、到臨近的鐵路運(yùn)輸線��、再到全球市場(chǎng)—從而重現(xiàn)了美國(guó)南北戰(zhàn)爭(zhēng)前的波士頓地區(qū)的資源消費(fèi)模式���,試圖探尋一個(gè)不同視角下的氣候控制、工業(yè)化�,以及城市(或城郊)資源系統(tǒng)等方面的歷史。
本文以該項(xiàng)目的原起以及用于追溯梭羅與物質(zhì)世界的對(duì)立的研究為主要內(nèi)容����。“重繪瓦爾登”是本研究中的一個(gè)章節(jié)���,試圖通過(guò)地圖繪制重現(xiàn)梭羅所描繪的1846年的采冰貿(mào)易�����。運(yùn)用科學(xué)史�����、統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)�、測(cè)量學(xué)以及后結(jié)構(gòu)主義建筑理論中直接和間接的資料���,本文對(duì)這一與景觀都市主義中常見(jiàn)的全球尺度量化地圖法以及過(guò)程圖形化相呼應(yīng)的題目進(jìn)行了探索��。如同凱勒?伊斯特林的《番茄世界》或皮埃爾?比朗格爾的一系列當(dāng)代景觀研究��,“邊緣運(yùn)作”或“林中物流”項(xiàng)目強(qiáng)調(diào)了存在于(走向工業(yè)化的)農(nóng)業(yè)中的潛在挑戰(zhàn)����、社會(huì)經(jīng)濟(jì)矛盾以及政治決策過(guò)失等各個(gè)方面之間復(fù)雜���、動(dòng)態(tài)以及基于過(guò)程的聯(lián)系���。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
瓦爾登湖;全球化����;物流;田園風(fēng)格;測(cè)繪��;都市主義
Abstract ...
Despite recent Landscape Urbanist interest in agrarian utopias and dispersed settlement strategies, Walden, or Life in the Woods, a canonic conservation text, is still often read as an inward-looking, pastoral experiment. My current project, Edge Operations or Logistics in the Woods, ‘runs the numbers’ from Walden. Appropriating Thoreau’s peri-urban position, Edge Operations works outward from Walden Pond — from woodlots to fireplaces, adjacent rails to global markets — re-constructing the (domestic) consumption patterns of antebellum Boston for an alternate history of climate control, industrialization, and its (sub)urban resource systems.
This essay describes the origin of this project and the research used to trace Thoreau’s material encounters. Excerpts from “Re-Surveying Walden”, one chapter of the project, map Thoreau’s descriptions of the ice harvest of 1846. These, with primary and secondary sources — in history of science, statistics, surveying and post-structural architectural theory — are explored for their resonance with quantitative, global mappings and the process diagrams typical of landscape urbanism. As in Keller Easterling’s Tomato World or Pierre Bélange’s contemporary research, Edge Operations or Logistics in the Woods highlights the complex, dynamic, and process-based alliances of (industrializing) agriculture, its lurking contests, socio-economic conflicts, and political culpabilities.
Key words ...
Walden; Globalization; Logistics; Pastoral; Mapping; Urbanism
曼谷水文和農(nóng)業(yè)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的重新構(gòu)想
Re-envisioning Bangkok’s Hydro and Agro Network
作者:川?蘇帕旺斯 Author: Chon SUPAWONGSE
摘要 ……
作為一個(gè)擁有動(dòng)態(tài)潮汐變化和快速城市化發(fā)展背景的地區(qū)����,湄南河河口340km2的廢棄水產(chǎn)養(yǎng)殖景觀為那些旨在應(yīng)對(duì)城市擴(kuò)張、生態(tài)衰退���、水文漲落���、淡水供應(yīng),食物生產(chǎn)以及廢物處理等多重挑戰(zhàn)的景觀設(shè)計(jì)干預(yù)提供了新的機(jī)會(huì)�。水是一種活躍機(jī)體。潮汐過(guò)程的引入是恢復(fù)多樣化生態(tài)性能��、支撐經(jīng)濟(jì)和推動(dòng)曼谷潮間帶景觀的城市轉(zhuǎn)型的一種城市設(shè)計(jì)途徑��。建立等級(jí)和水文分流意在提升城市適應(yīng)多種水文情況的能力�,而非對(duì)水文情況加以控制或逆之而為。作為一座位于季風(fēng)河口地帶的城市�,曼谷必須是柔軟的、吸納力強(qiáng)且具有適應(yīng)性的����。該項(xiàng)目的操作策略可以應(yīng)用于現(xiàn)存的其他水文和農(nóng)業(yè)網(wǎng)絡(luò),以建立一種能夠體現(xiàn)綜合性的水文生態(tài)功能,并能夠應(yīng)對(duì)多種時(shí)間跨度和空間維度上的環(huán)境變化的新的景觀基礎(chǔ)設(shè)施����。
關(guān)鍵詞 ……
河口;動(dòng)態(tài)變化���;流動(dòng)性����;層級(jí)��;操作
Abstract ...
As a conjunction of tidal dynamics and rapid urbanization, 340 square kilometers of the derelict aquacultural landscapes on the Chao Phraya Estuary offers a fresh opportunity for a landscape architectural intervention in addressing multiple challenges of urban expansion, decaying ecology, hydrologic fluctuation, freshwater supply, food production and waste. Water is an active agency. Introduction of tidal process is an urban program device that reactivates diverse ecological performances, underpin economics, and drive urban transformation over Bangkok’s intertidal landscape. Creation of levels and hydrologic distributaries aims to engage adaptability to multiple water regimes rather than control or work against it. Bangkok, the city in the monsoon estuary must be soft, absorbent and adaptive. The operative strategies of this project can be applied to the remaining hydro and agro network to build a new landscape infrastructure that performs mixed hydro-ecological functions and responses to environmental shifts in diverse range of times and spatial scales.
Key words ...
Estuary; Dynamics; Fluidity; Level; Operation
 京公海網(wǎng)安備 110108000058號(hào)
京公海網(wǎng)安備 110108000058號(hào)