1993年和1995年�,荷蘭林堡省的默茲河發(fā)生了兩次令人震驚的大洪水,自1926年以來(lái)從未出現(xiàn)過(guò)如此高的水位�,經(jīng)濟(jì)損失巨大。1996 年該地區(qū)采取了臨時(shí)措施�,如修建應(yīng)急堤壩,關(guān)閉奧延鎮(zhèn)和萬(wàn)瑟姆鎮(zhèn)之間的舊河道Oude Maasarm等�����,以期在短期內(nèi)保障該地區(qū)的水安全�����。但從長(zhǎng)遠(yuǎn)來(lái)看,這些臨時(shí)措施是不夠的�。
In 1993 and 1995, the Dutch province of Limburg was startled by two major floods of the Meuse. Such highwater levels had not occurred since 1926 and the economic damage was enormous. Temporary measures were taken in 1996 to improve the water safety of the area in the short term: emergency dikes were constructed in various places and the old river course between Ooijen-Wanssum, the ‘Oude Maasarm’ was closed. In the long term, these temporary measures however are not sufficient.
▼萬(wàn)瑟姆鎮(zhèn)遠(yuǎn)眺
Centrum Wanssum ? Paul Poels
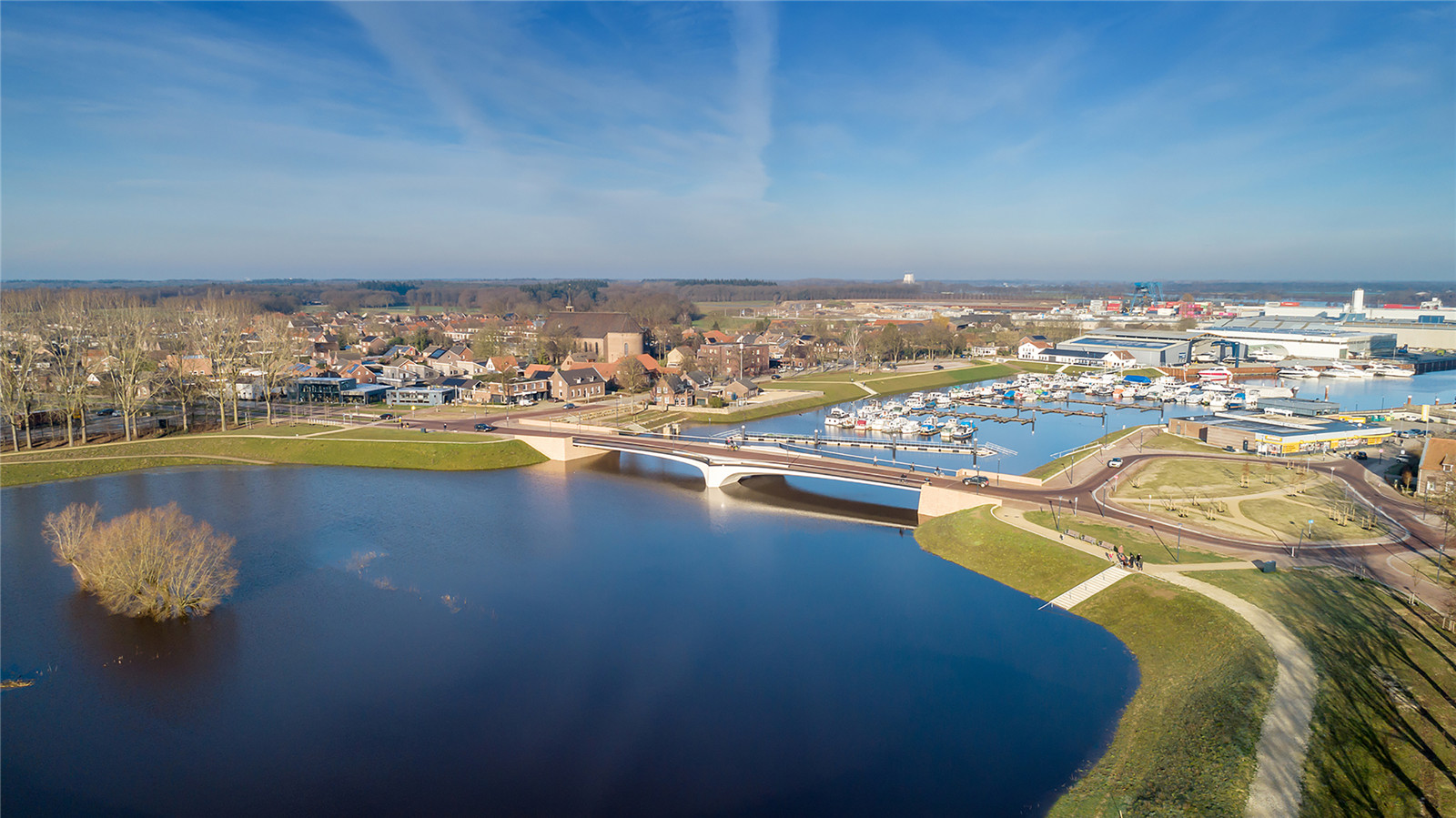

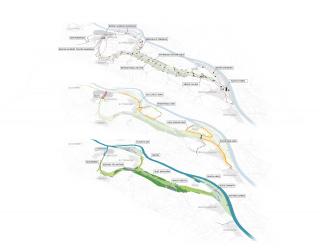
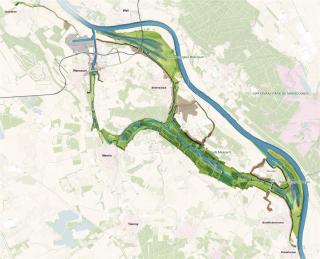
▼設(shè)計(jì)區(qū)域平面圖
Plan Ooijen Wanssum ? H+N+S Landscape Architects
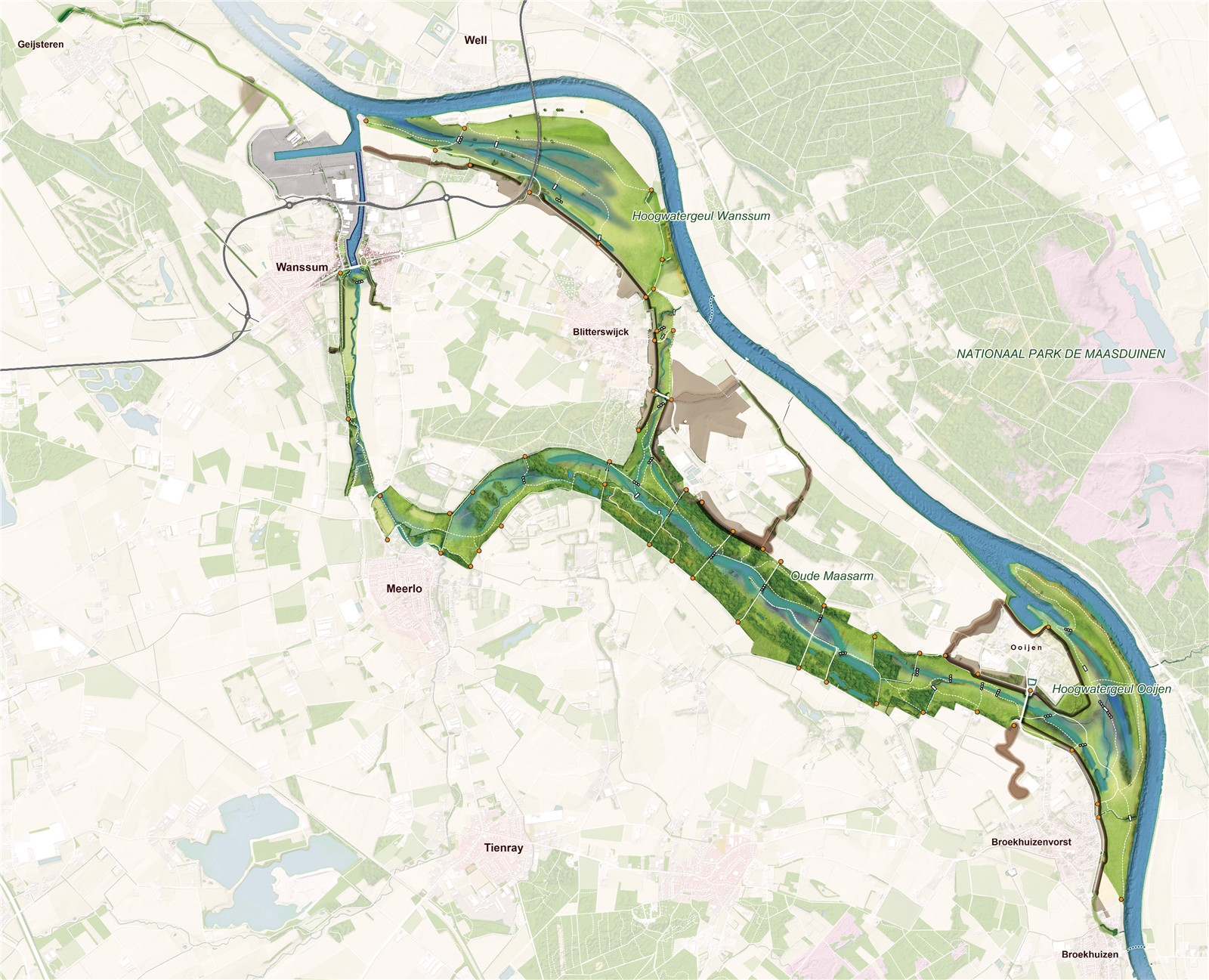
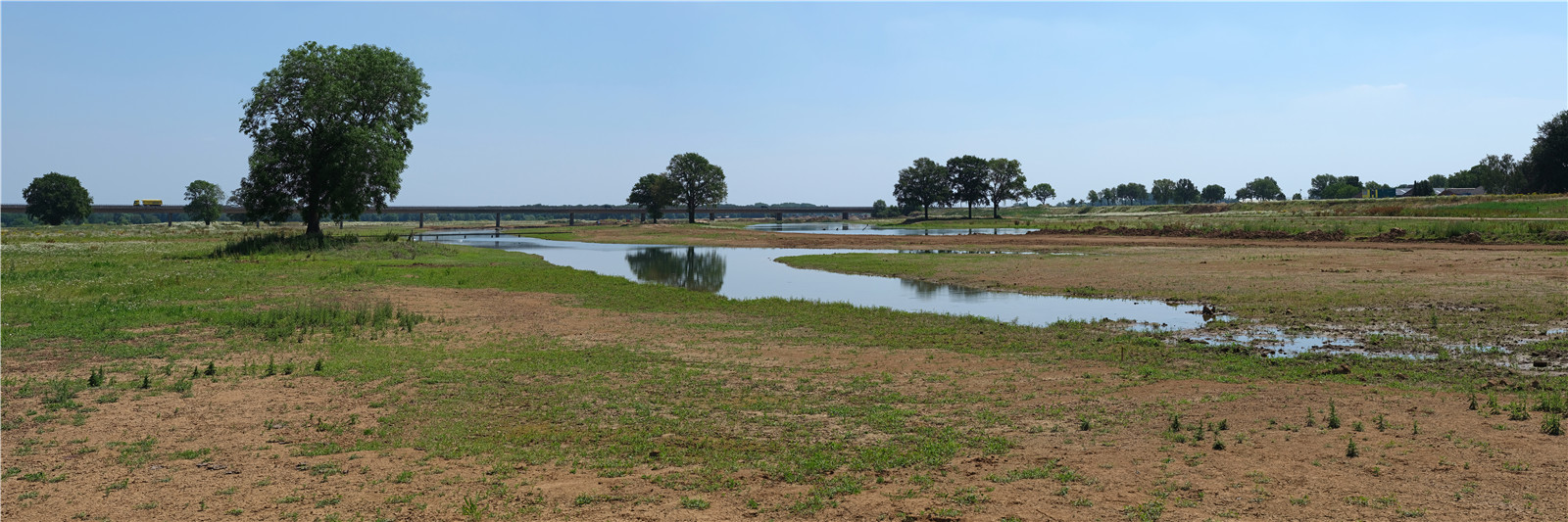
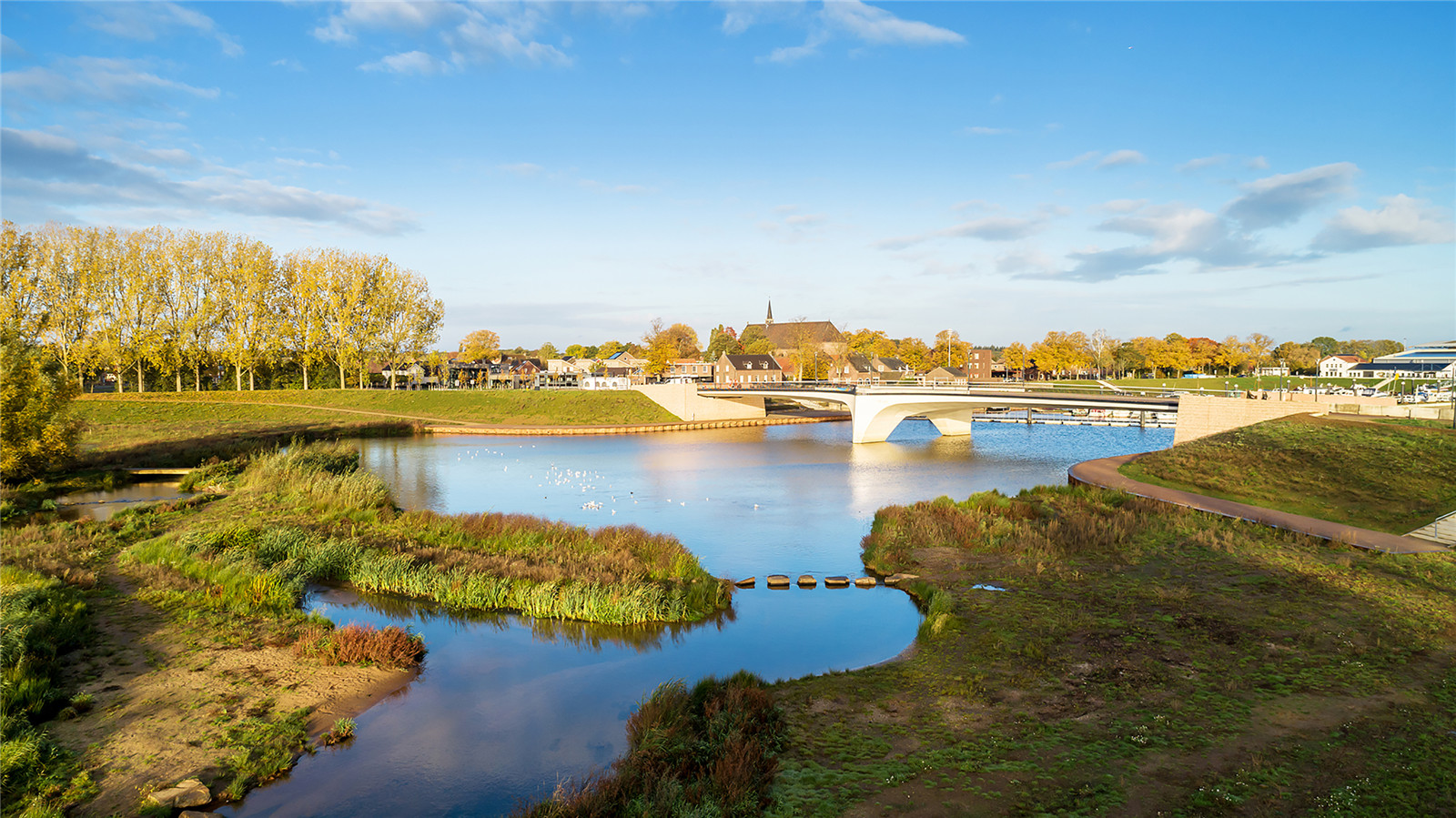
項(xiàng)目在建設(shè)堤壩的同時(shí)將河道拓寬,從而更好地保護(hù)該地區(qū)免受高水位影響���。項(xiàng)目新建了20多公里的堤壩�,同時(shí)通過(guò)降低Weerd河漫灘高度���、重新打通Oude Maasarm河道等措施�,使水位下降了35厘米���。此外���,項(xiàng)目還增加了超過(guò)300公頃可供人們使用的自然植被覆蓋區(qū),精細(xì)的地面高差設(shè)計(jì)為草地�����、長(zhǎng)滿蘆葦?shù)臐竦睾蜑I水森林的發(fā)展提供了最佳條件�。最后,新環(huán)路建設(shè)使萬(wàn)瑟姆鎮(zhèn)的生活品質(zhì)得以提高�,而城鎮(zhèn)中心空間的重新設(shè)計(jì)也為該地區(qū)注入了新的經(jīng)濟(jì)活力�。項(xiàng)目建成后����,為該地區(qū)帶來(lái)了空間和生活上的雙重提升��。
With this project, the area is better protected against high water by a combination of dike construction and river widening. More than 20 km of new dikes are constructed and a 35 cm drop in water level is realized by lowering the ‘weerd’ (floodplain along the river) and by reactivating the ‘Oude Maasarm’. In addition more than 300 hectares of new, freely accessible nature is realized: with a sophisticated ground level design, the optimal conditions are offered for the development of special grasslands, sedge swamps and river forests. Finally, the quality of life in the town of Wanssum is increased by the construction of a new ring road and the redesign of the town center and space is created for new economic developments in the area. Both the spatial quality and the quality of life are boosted as a result of this project.
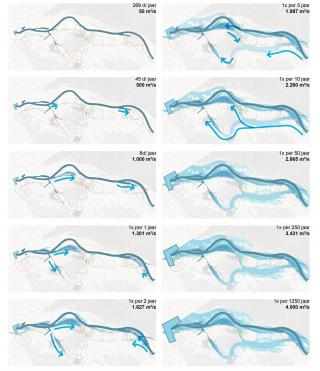
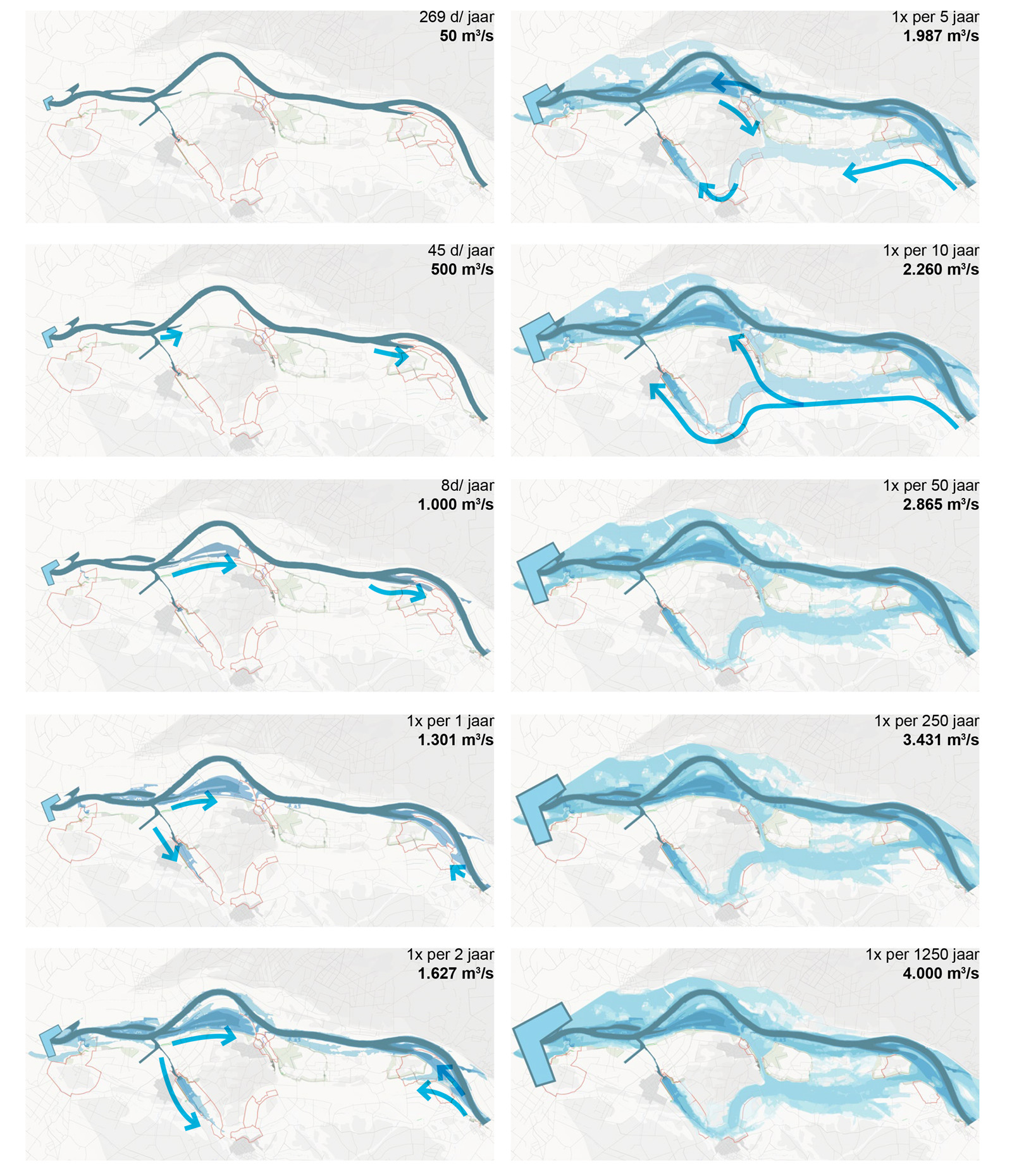
▼不同流量下的水流方向
The water calendar with flow directions ? H+N+S Landscape Architects
▼設(shè)計(jì)提升了河流兩岸的景色品質(zhì)
Project brings a higher quality of landscape along the Meuse ? Paul Poels
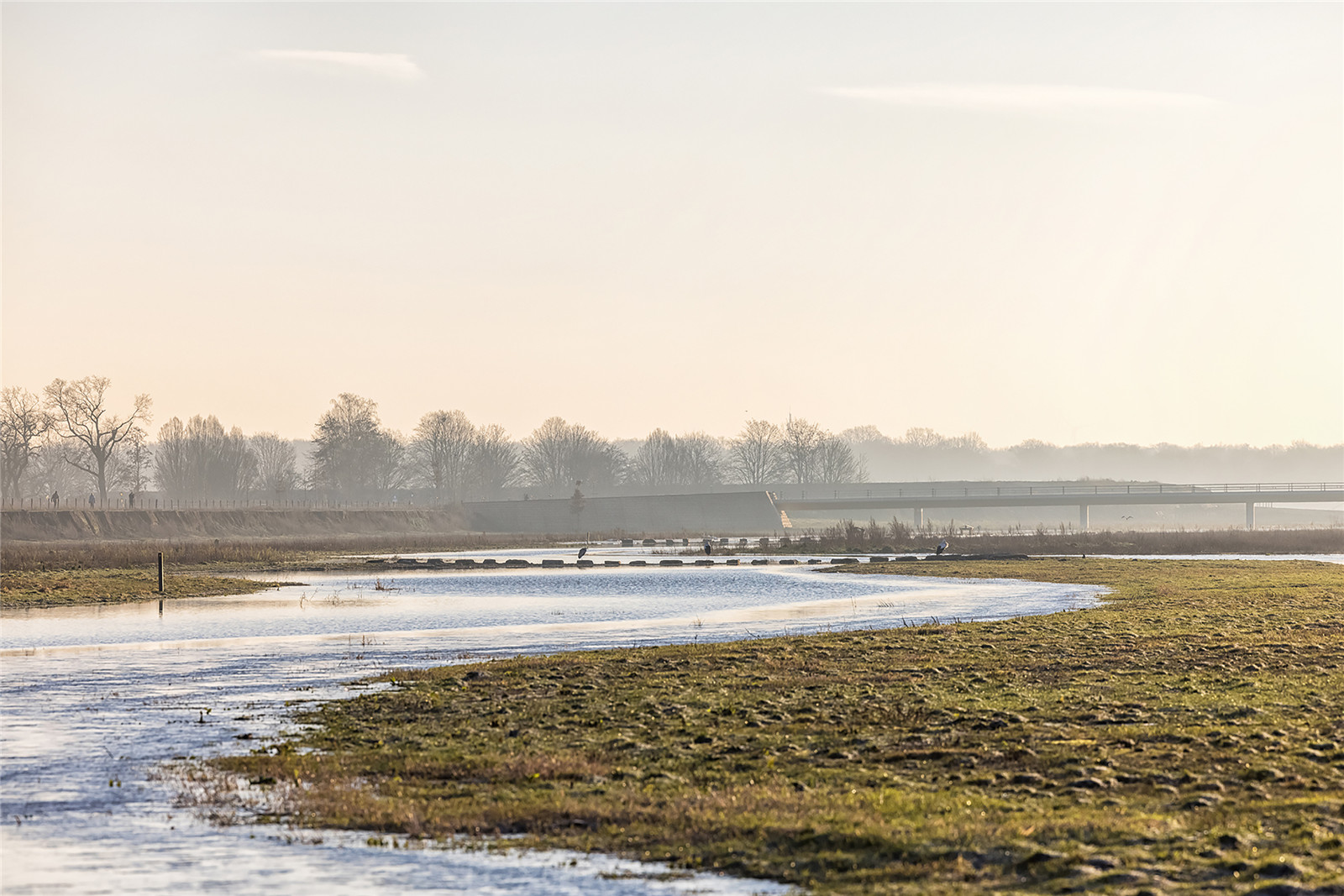

項(xiàng)目的獨(dú)到之處在于其規(guī)劃的完整性��、各參與方的緊密合作以及對(duì)空間質(zhì)量和創(chuàng)新的高度關(guān)注����。其中最引人注目和最有價(jià)值的部分是其全新且獨(dú)特的堤壩加固方法。
What is special about the project is the integrality of the plan, the close cooperation between all parties involved and the high degree of attention to spatial quality and innovations. Most striking and priceworthy part of the design is a new and unique approach to the dike reinforcement task.
▼陡坡堤壩和降低的河漫灘
construction of the steep edge dike and lowering of the flood plains ? Siebe Swart
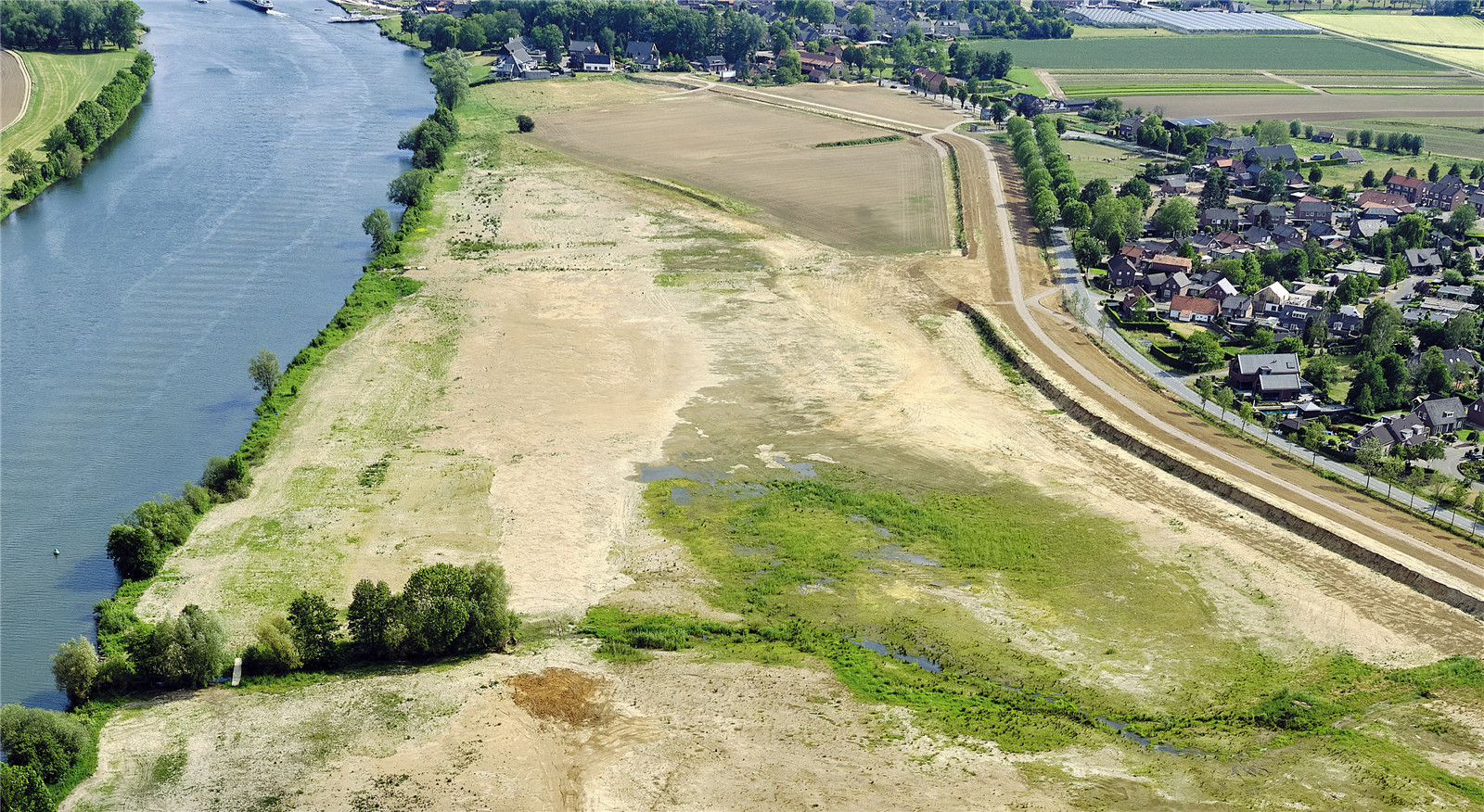

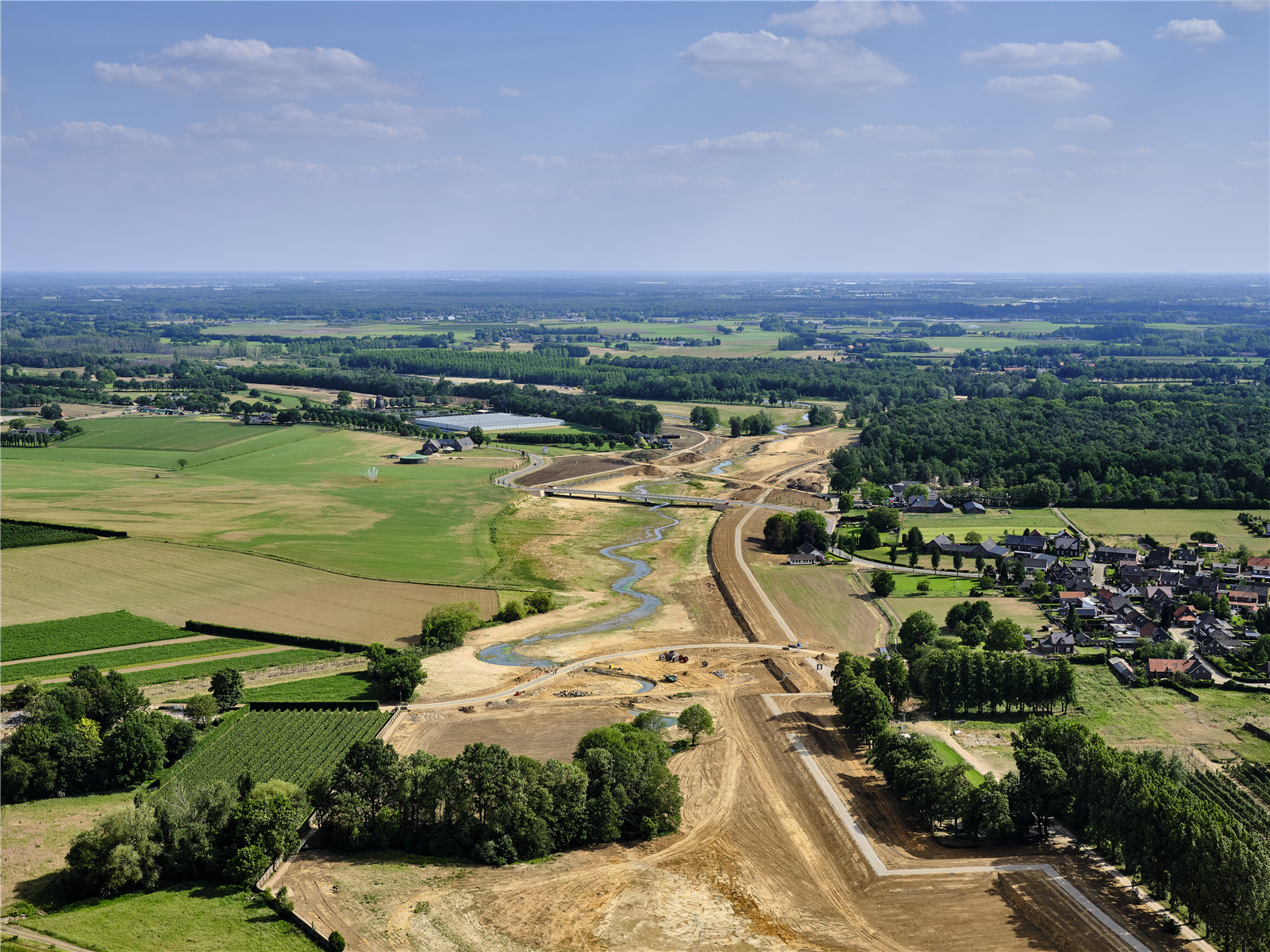
▼區(qū)域航拍
aerial photo ? Siebe Swart
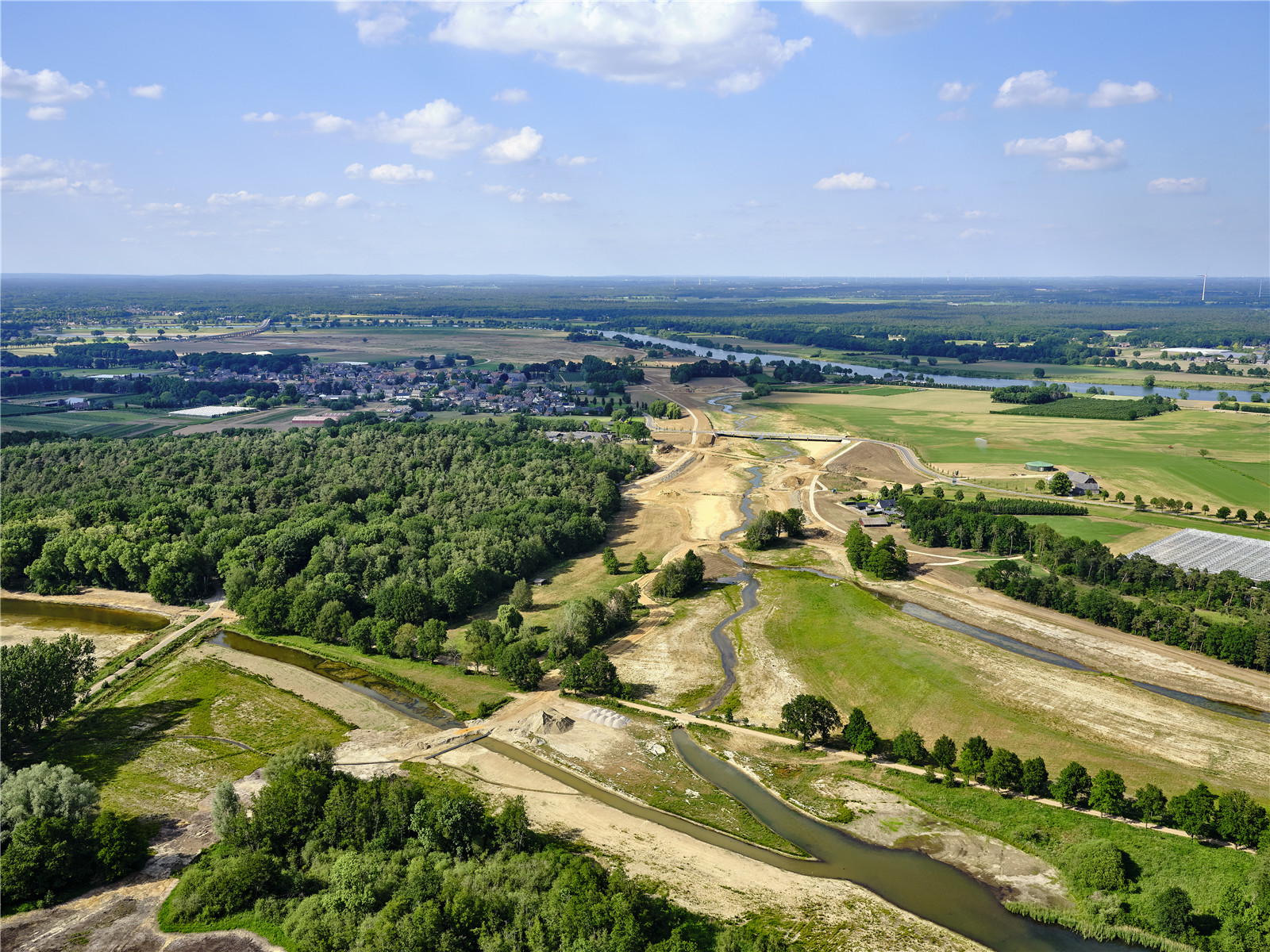

1996年修建的應(yīng)急堤壩之前����,默茲河從未建設(shè)過(guò)堤壩,因此河流兩岸保留著傳統(tǒng)的臺(tái)地景觀��。為了避免破壞這一特質(zhì)�,設(shè)計(jì)團(tuán)隊(duì)設(shè)想了兩種既能保障水安全,又能融于景觀之中的堤壩設(shè)計(jì)方案�����,即“陡坡堤壩”和“高地堤壩”����。
With the dike design a solution has been devised for water safety without affecting the traditional terraced landscape of the Meuse, that until the construction of the emergency dikes in 1996 never included dikes. To this result two new dike types were developed that merge into the landscape: the ‘steep-edge dike’ and the ‘high ground dike’.
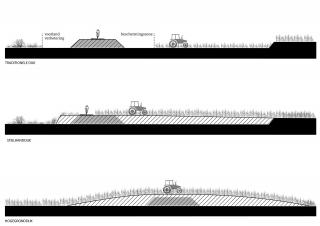
▼傳統(tǒng)堤壩與新堤壩對(duì)比
scheme traditional dike vs new dike types ? H+N+S Landscape Architects
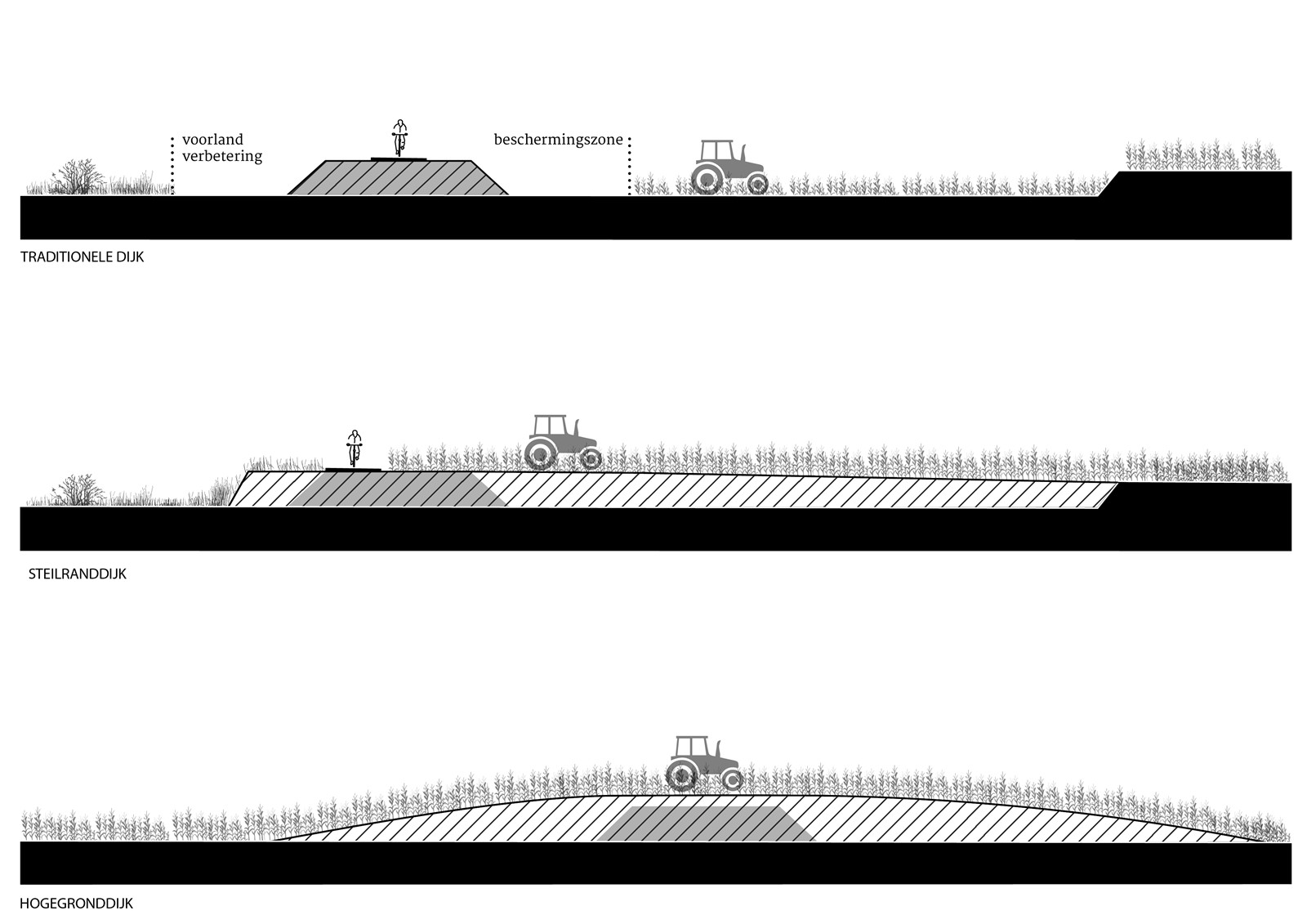
新堤壩占據(jù)的凈空間更小����,卻能提供更多的使用可能性����,如農(nóng)業(yè)耕種和重新造林等,同時(shí)也更易于管理�����。堤壩的筑造材料來(lái)自于降低河漫灘高度時(shí)多余的土壤��,幾乎實(shí)現(xiàn)了區(qū)域的土方平衡�,且避免了對(duì)環(huán)境造成負(fù)面影響的深砂開(kāi)采,降低二氧化碳排放����,減少?gòu)暮勇┣宄寥篮偷虊沃煊猛恋某杀尽榱藢?shí)現(xiàn)這一創(chuàng)新��,我們與水資源管理委員會(huì)密切合作��,在德國(guó)漢堡的流體力學(xué)實(shí)驗(yàn)室對(duì)堤壩進(jìn)行了測(cè)試����。
The new dikes have a smaller net space requirement, more usage possibilities including arable farming and reforestation and a smaller management burden for the Water Board. The dikes are made with local soil that is released during the lowering of the floodplains. This makes it possible to achieve a virtually closed ground balance. Deep sand extraction with its negative environmental impact is avoided as well as large (CO2) emissions and costs of the removal of enormous amounts of soil from the floodplains and the supply of dike clay. In order to realize this innovation, we worked very closely with the water board and the dikes were tested in a hydrodynamic laboratory in Hamburg.
陡坡堤壩
Steep-edge dike
▼陡坡堤壩剖面圖
principal profile steep edge dike ? H+N+S Landscape Architects
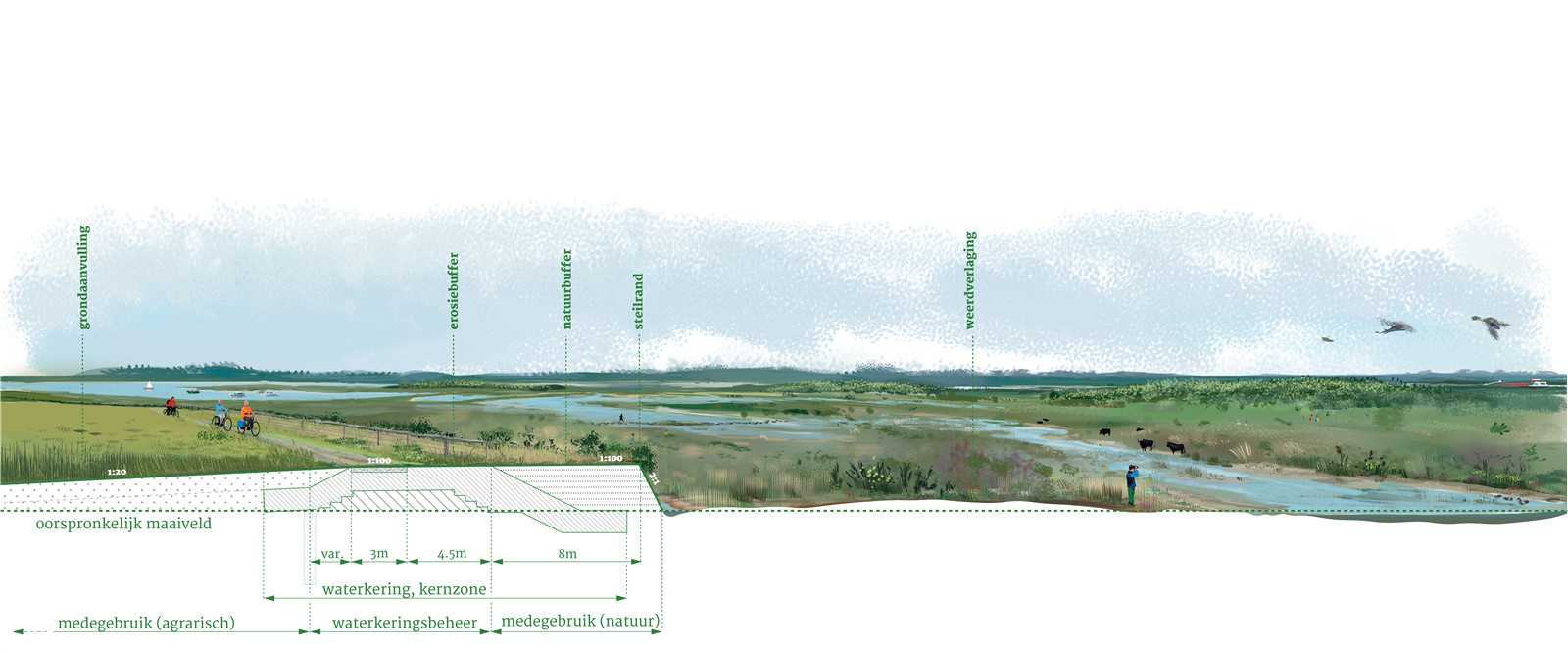
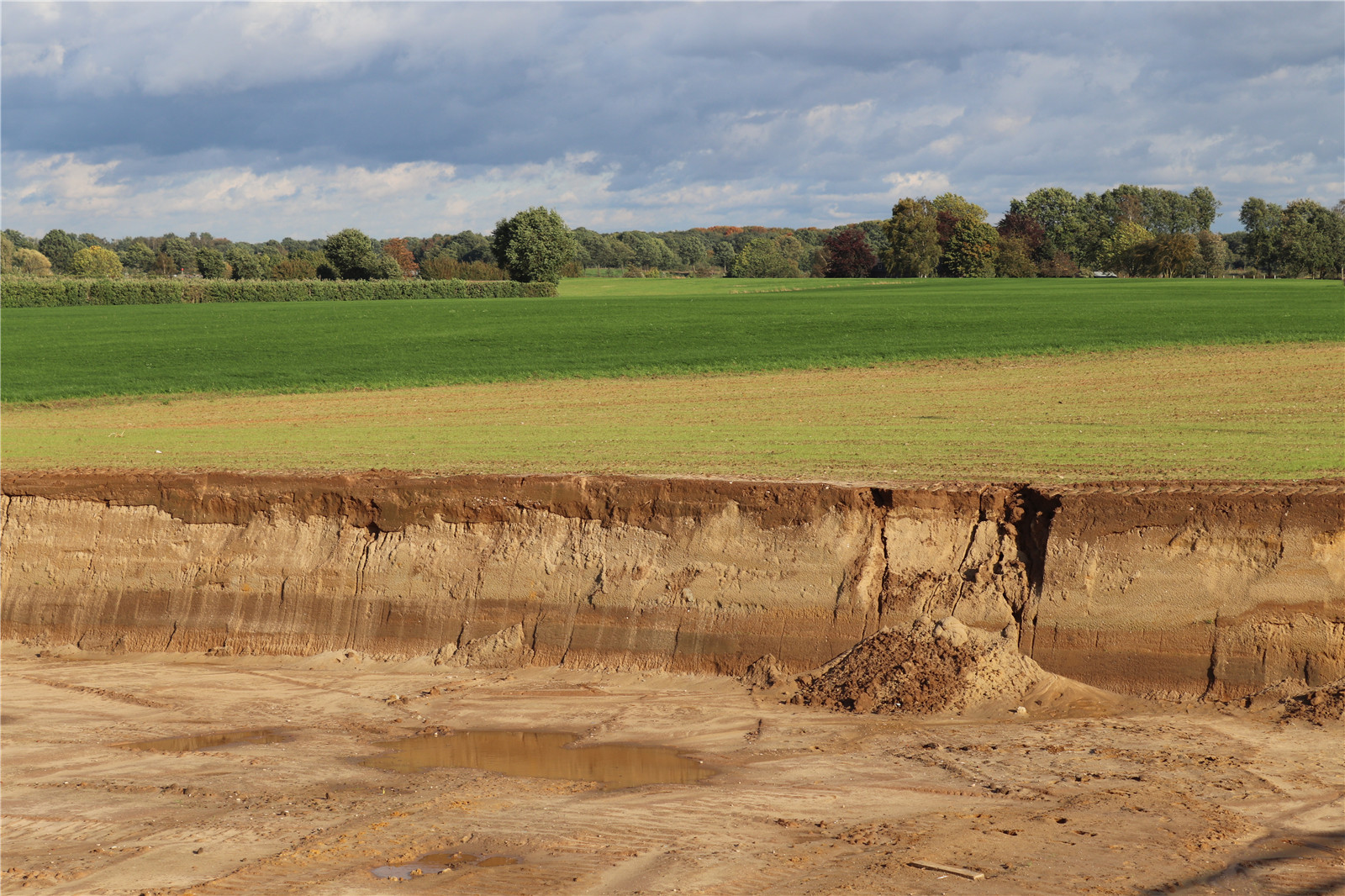
陡坡堤壩不對(duì)稱的輪廓�����,正與默茲河岸那時(shí)而平緩時(shí)而陡峭的自然地貌相契合�。設(shè)計(jì)團(tuán)隊(duì)將其設(shè)置于中上臺(tái)地到下層臺(tái)地的過(guò)渡處�����,成為新自然保護(hù)區(qū)的邊界����。堤壩面向河流的邊緣是坡度高達(dá)2:1的放坡�,它接納自然侵蝕的過(guò)程,如樹木等植被覆蓋�、放牧大型食草動(dòng)物和水流侵蝕等,不僅外觀天然有趣��,還具有較高的生態(tài)價(jià)值��。自然保護(hù)區(qū)的入口仿佛堤壩上的切口��。為了保證水安全�����,在這個(gè)“天然緩沖區(qū)”后面,設(shè)計(jì)團(tuán)隊(duì)用當(dāng)?shù)夭牧辖ㄔ炝艘粋€(gè)強(qiáng)大的“侵蝕緩沖區(qū)”����,取代了傳統(tǒng)防洪的粘土層和草地覆蓋層。堤壩面向內(nèi)側(cè)的斜坡坡度至少為1:8�����,盡可能達(dá)到1:20����,并填充封閉的低洼區(qū)域,這些做法將改善農(nóng)業(yè)條件和水利系統(tǒng)�,當(dāng)前的土地利用方式可以在這個(gè)斜坡上繼續(xù)進(jìn)行。
The steep-edge dike has an a-symmetrical profile that fits in with the natural relief of the Meuse landscape, which only has gentle or steep relief transitions. The steep-edge dike is implemented at the transition from the upper middle terrace to the lower terrace, on the border of the new nature reserve. This boundary is shaped like a steep edge with a 2:1 slope. Natural erosion processes are allowed in this steep edge, creating an interesting, natural image with high ecological value. Vegetation with trees, grazing with large grazers and erosion are no problem. The entrances to the nature reserve are strikingly designed as incisions in the dike. To guarantee water safety, a strong ‘erosion buffer’ of local materials is built behind this 'natural buffer', replacing the clay layer and grass cover of a traditional flood defense. At the inside of the dike a slight slope is constructed at least 1:8, preferably 1:20 and enclosed lower areas are filled, which will improve agricultural conditions and the water system. The current land use can be continued on this slight slope.
▼建設(shè)中的陡坡堤壩和橋墩
construction of steep edge dike and bridge bastions ? Hans van der Meer
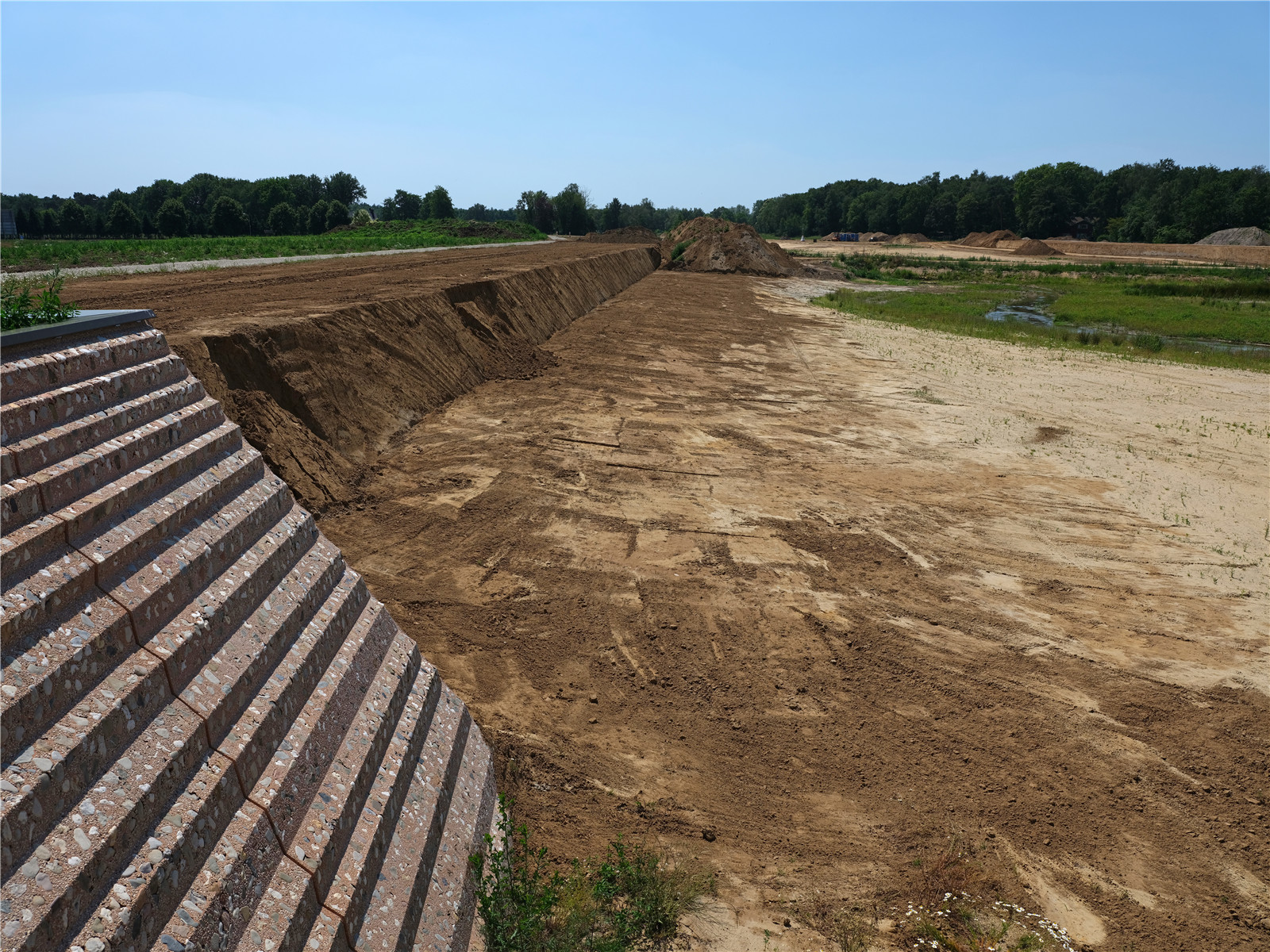

▼地勢(shì)較低的河漫灘背后是陡坡堤壩
lowerd flood plains with steep edge dike in background ? Hans van der Meer

▼陡坡堤壩允許被侵蝕
The steep-edge dike is allowed to erode ? H+N+S Landscape Architects

端莊且標(biāo)志性的新橋梁橫跨Oude Maasarm河����,橋梁就地澆筑,因其纖細(xì)的設(shè)計(jì)�����、與景觀的契合而聞名�����。橋頭設(shè)計(jì)為堡壘形式,以便與堤壩區(qū)別開(kāi)�。
New, modest yet iconic cross the Oude Maasarm. The bridges are cast in situ and are notable for their slender design, subordinate to the landscape. The bridge heads form distinctions on the dike as bastions.
▼標(biāo)志性的橋梁
iconic bridges ? Paul Poels

▼自然保護(hù)區(qū)與橋梁
new nature area and bridge ? Paul Poels
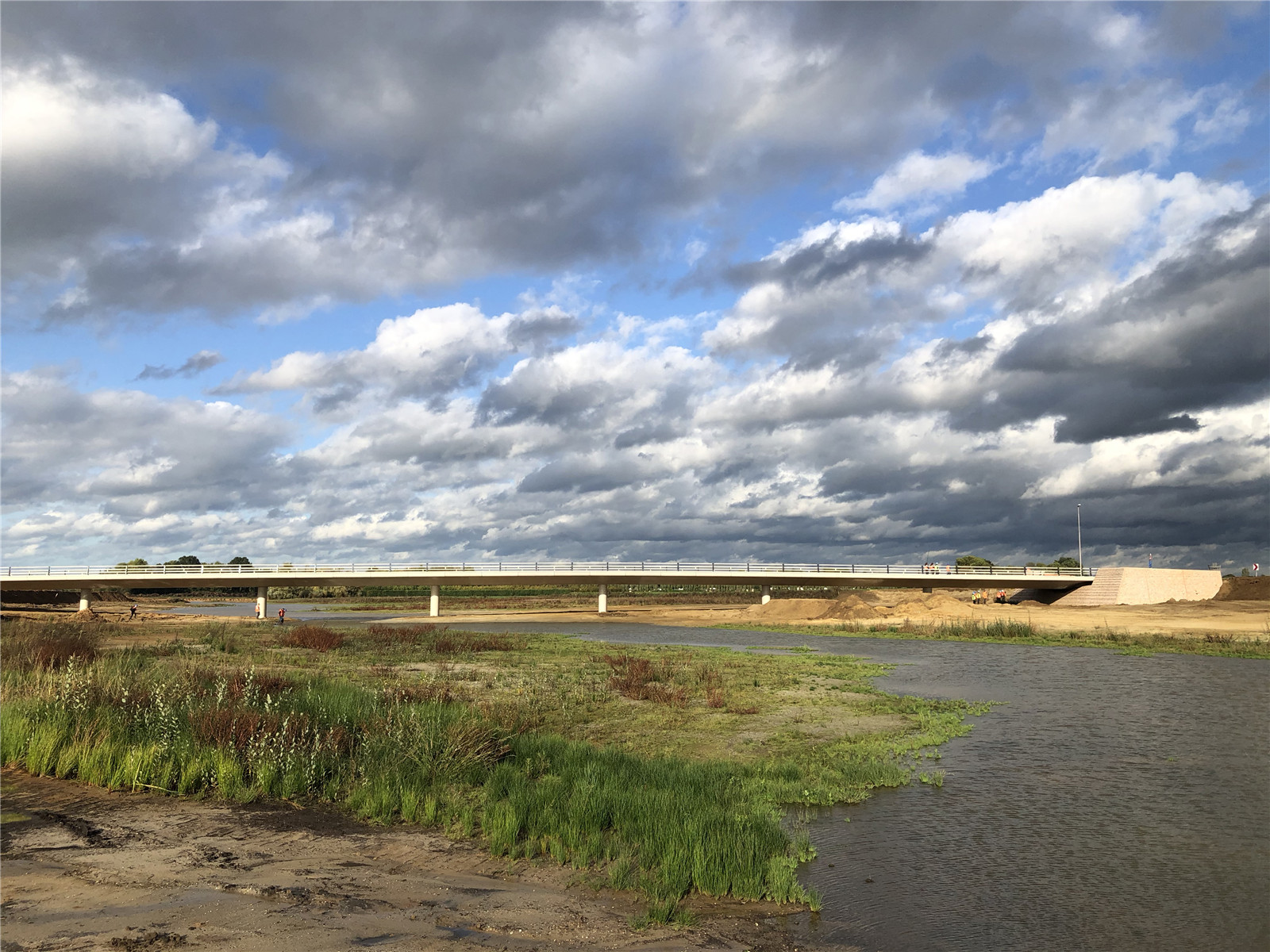


▼橋梁與陡坡堤壩
new bridge and village centre wanssum ? Hans van der Meer
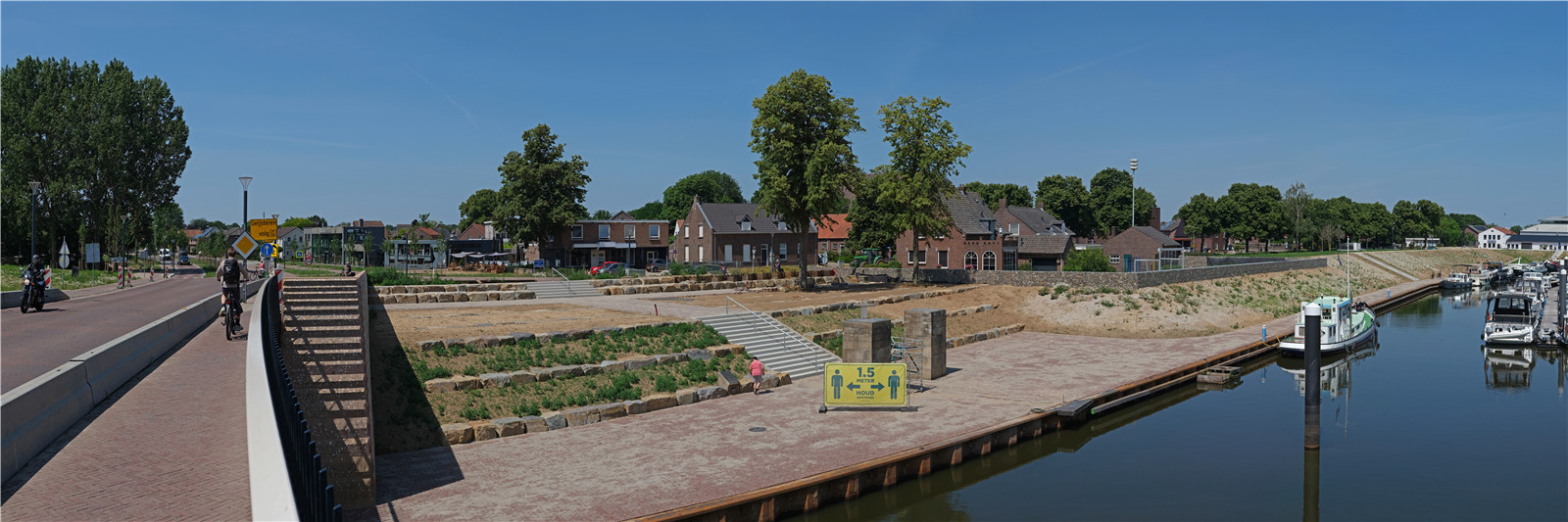

高地堤壩
High Ground dike
▼高地堤壩剖面圖
principal profile of high ground dike ? H+N+S Landscape Architects
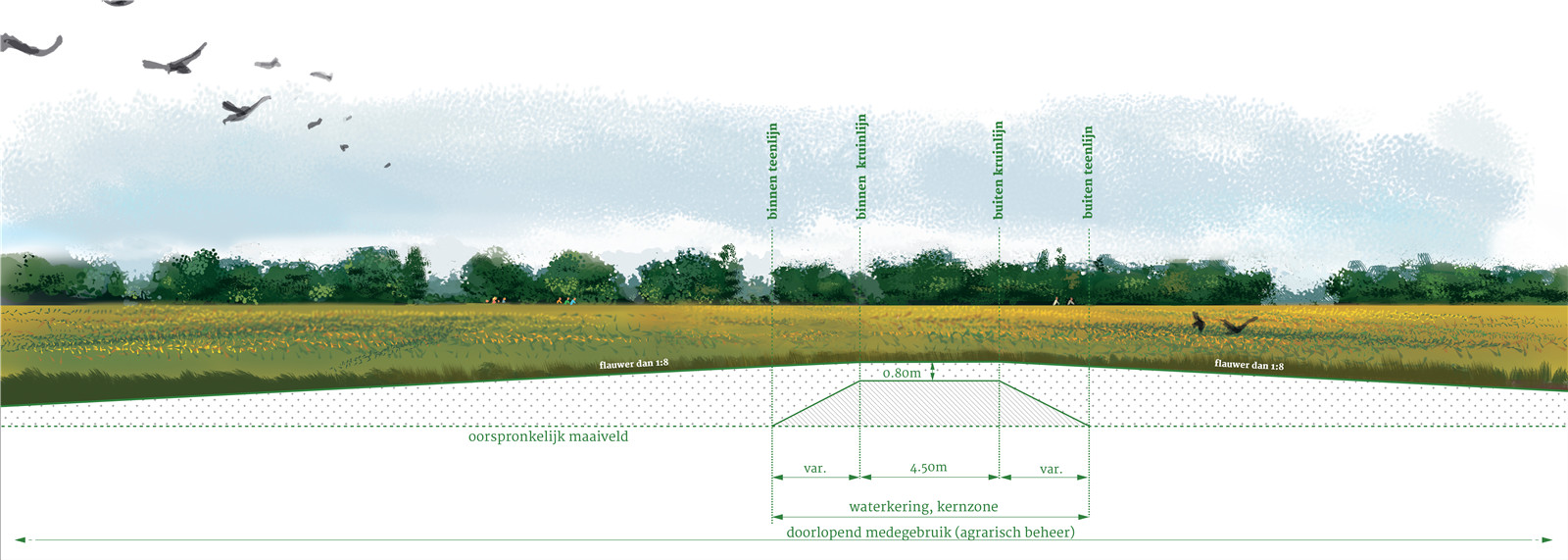
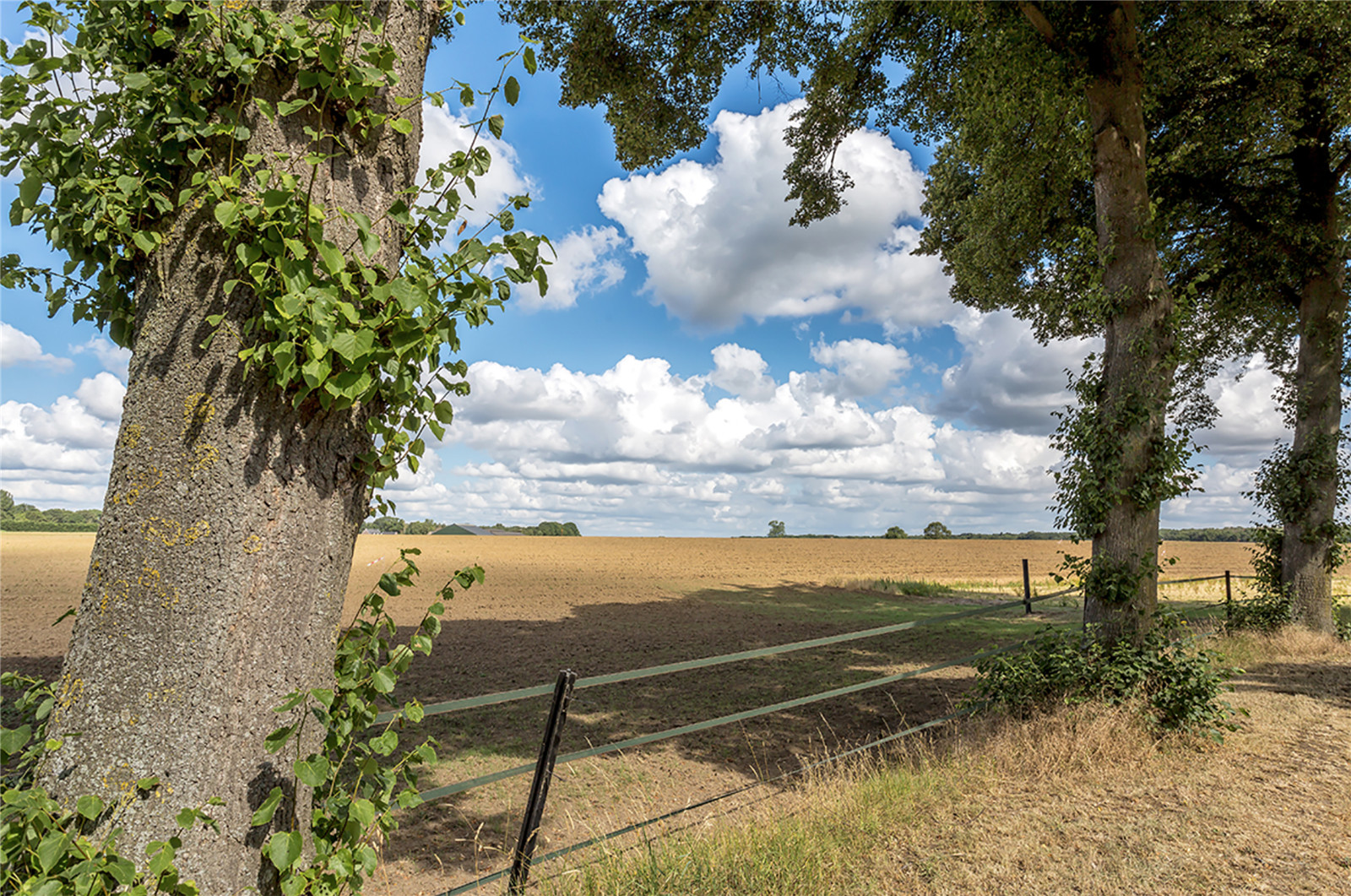
高地堤壩幾乎是看不見(jiàn)的,它完全融入了地形豐富的景觀之中�����。設(shè)計(jì)利用降低河漫灘時(shí)挖出的土壤��,在滿足技術(shù)上的防洪要求之外����,額外增加了堤壩的高度和寬度��。高低堤壩堅(jiān)固而具有前瞻性����,無(wú)需將其作為洪水防御系統(tǒng)進(jìn)行特殊維護(hù),而且可以自由地使用�����。這些堤壩可以繼續(xù)與第三方合作進(jìn)行農(nóng)業(yè)開(kāi)發(fā)����,或者覆蓋以森林�,建造時(shí)也不需要購(gòu)買土地����。高地堤壩用于堤壩系統(tǒng)需貫穿中層臺(tái)地的區(qū)域。
The high ground dike is an invisible dike, completely merging into the landscape which is rich in relief. With local soil from the lowering of the flood plains additional height and width are applied above the technically required profile of the flood defense. Due to this robust and future-proof profile, the high ground dike does not have to be maintained as a flood defense by the water board and there are no obstacles to its use. The dikes can remain in agricultural use with third parties and may even be overgrown by forest. An additional advantage is that no land needs to be purchased. The high ground dike is used on the sections where the dike runs straight across the middle terrace.
▼高地堤壩在景觀中消隱
the high ground dike invisible in the landscape ? H+N+S Landscape Architects

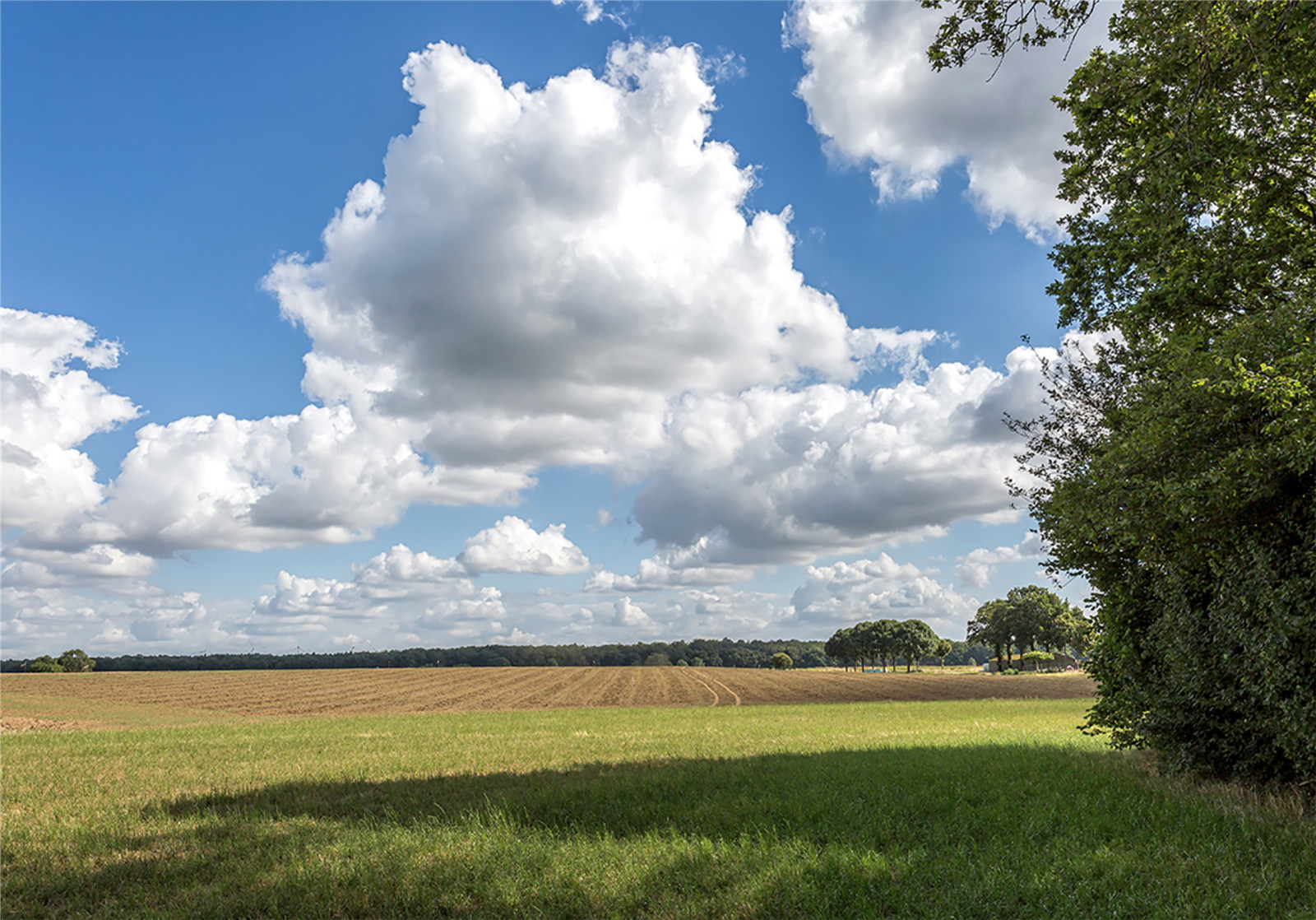
▼高地堤壩與景觀融為一體��,用于農(nóng)業(yè)栽培
the high ground dike merges in the landscape and is used for arable farming ? H+N+S Landscape Architects

為保持連貫性�,相鄰區(qū)域的堤壩類型是一致的。在一些特殊地段�����,如Blitterswijck的古城堡遺址附近����,或建筑靠近堤岸的地方,團(tuán)隊(duì)特別設(shè)計(jì)了部分堤壩����,讓觀景視野更加豐富。
For the sake of cohesion, the dike types are applied consistently. In special places, such as the old castle ruins at Blitterswijck or where buildings are close to the dike, customized work is provided which enriches the view.
▼高水位時(shí)觀景臺(tái)
look out tower at high tide ? Paul Poels

▼陡坡堤壩與古堡遺址相融合
steep edge dike and integration of old castle site bastion ? Siebe Swart

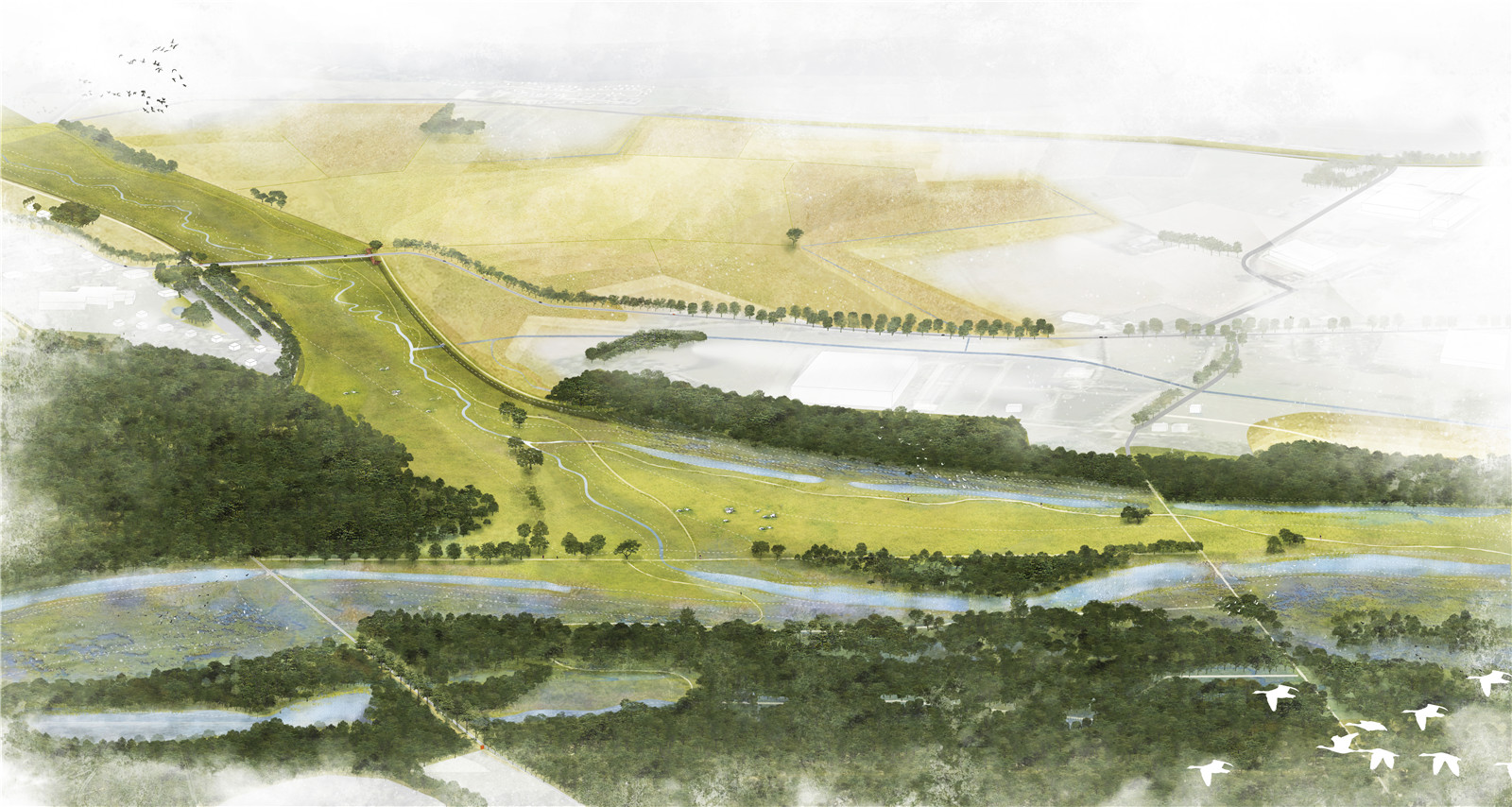
項(xiàng)目圖紙
▼Blitterswijck區(qū)設(shè)計(jì)意向
impression design area blitterswijck ? H+N+S Landscape Architects

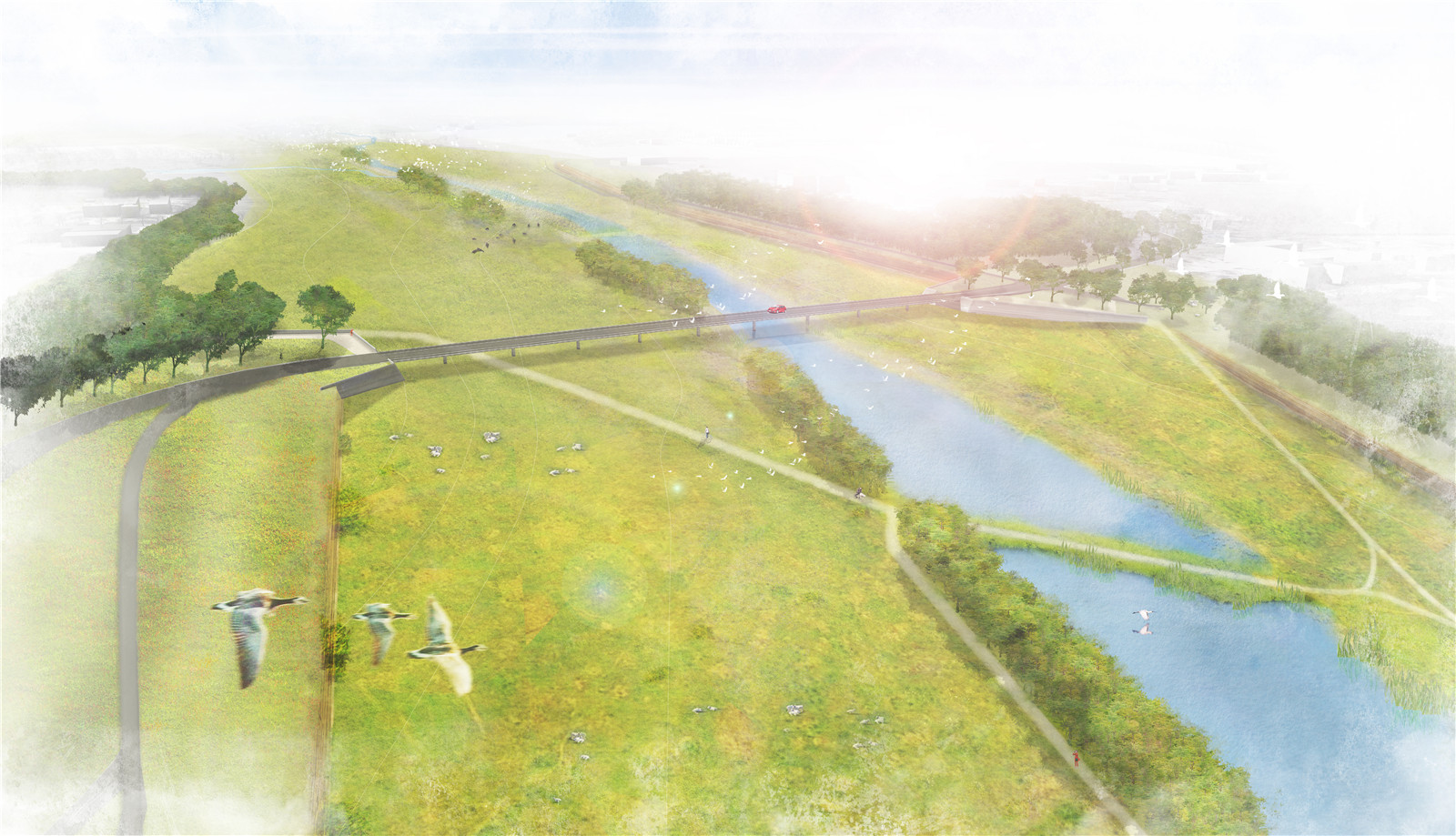
▼奧延區(qū)設(shè)計(jì)意向
impression design area ooijen ? H+N+S Landscape Architects

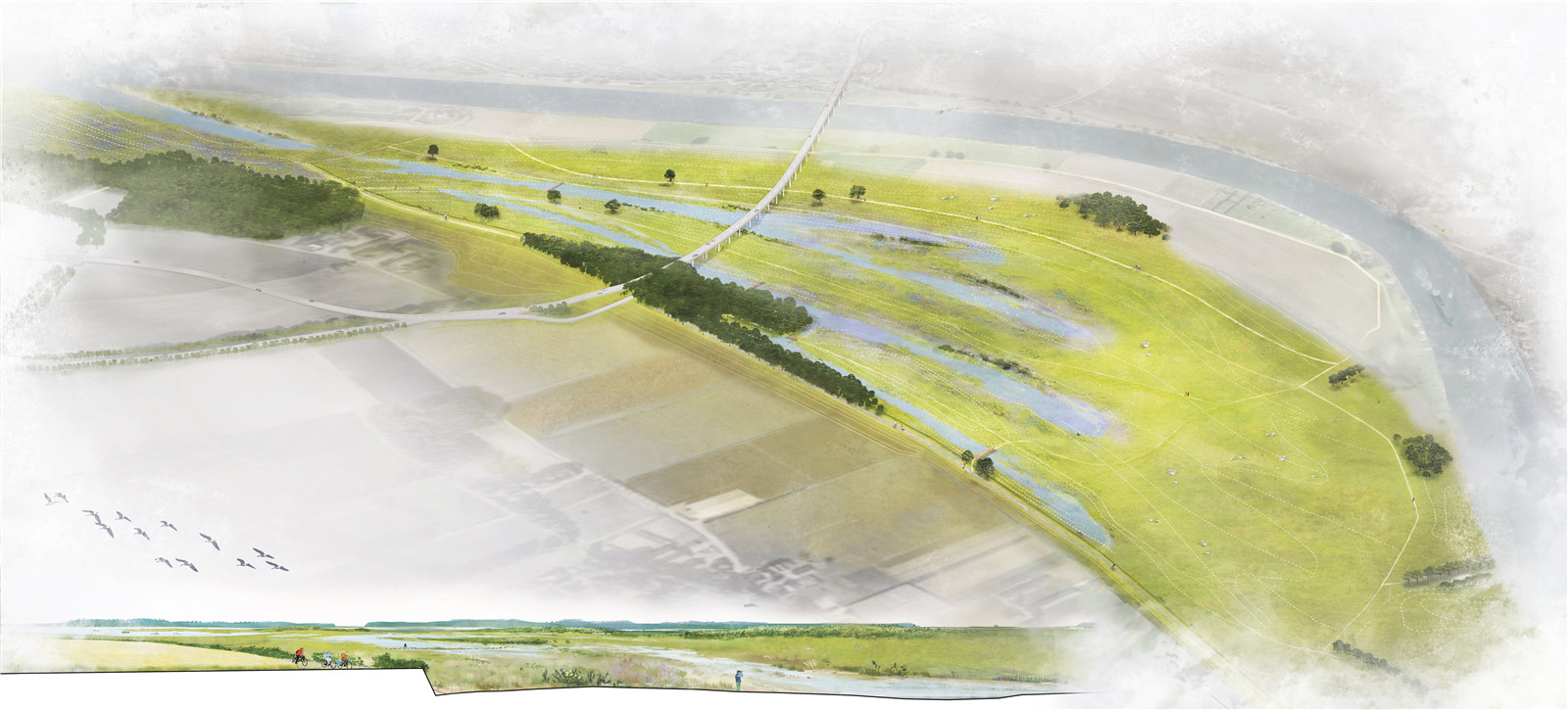
▼萬(wàn)瑟姆區(qū)設(shè)計(jì)意向
impression design area wanssum ? H+N+S Landscape Architects

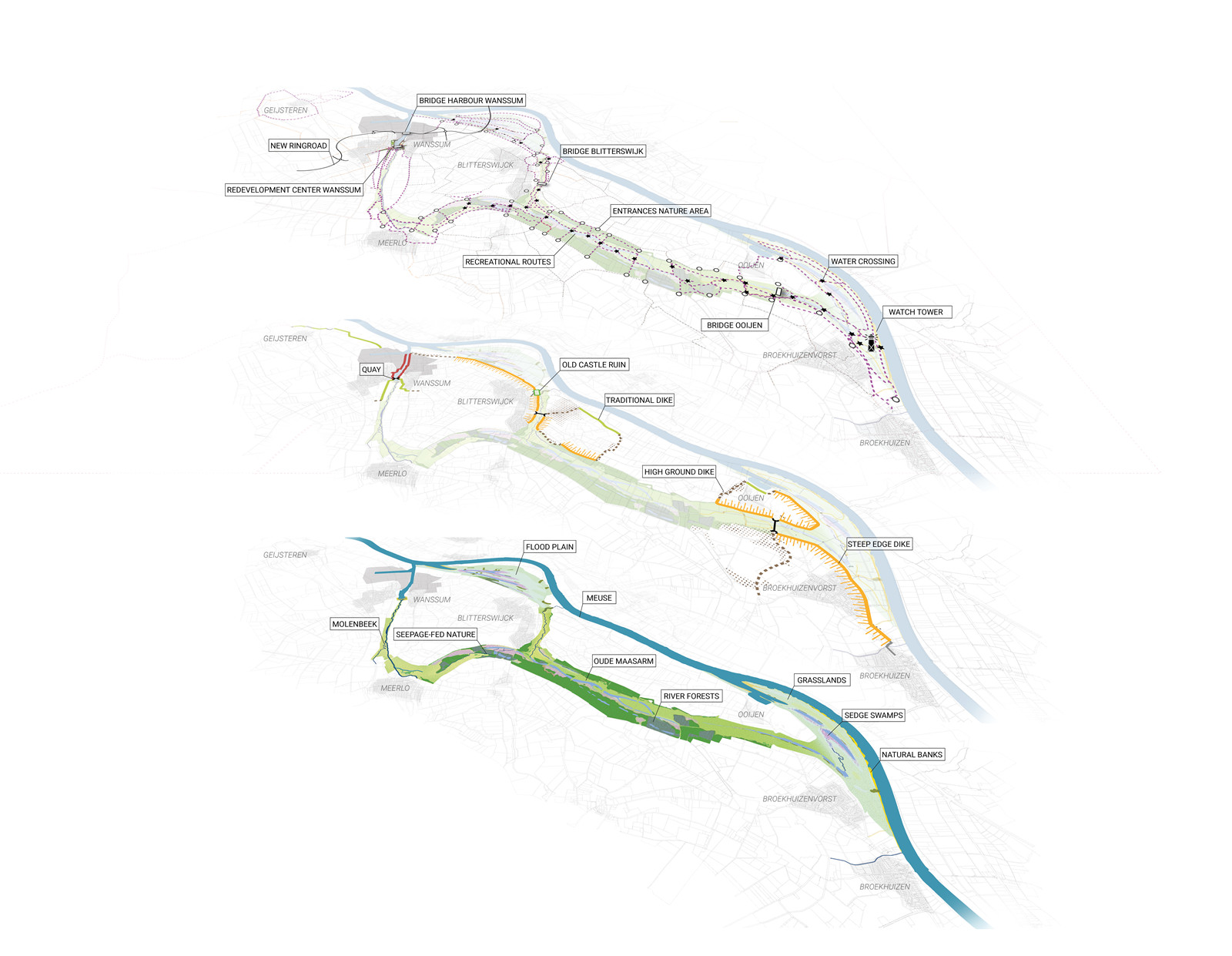
▼分層平面
plan in layers ooijen wanssum ? H+N+S Landscape Architects
項(xiàng)目信息
項(xiàng)目名稱:奧延-萬(wàn)瑟姆區(qū)域開(kāi)發(fā)
項(xiàng)目地點(diǎn):荷蘭林堡省奧延鎮(zhèn)至萬(wàn)瑟姆鎮(zhèn)
設(shè)計(jì)公司: H+N+S景觀事務(wù)所
委托方:林堡省政府����,芬賴市政府�,霍斯特安德馬斯市政府����,林堡省水委員會(huì),荷蘭水運(yùn)當(dāng)局
設(shè)計(jì)時(shí)間:2015-2020
建成時(shí)間:2017-2021
圖片來(lái)源:H+N+S Landscape Architects, Siebe Swart, Hans van der Meer, Paul Poels
所獲獎(jiǎng)項(xiàng):LILA 2021國(guó)際景觀獎(jiǎng) 基礎(chǔ)設(shè)施類
Project name: Area Development Ooijen-Wanssum
Location: Ooijen-Wanssum, Province of Limburg, the Netherlands
Landscape Architect: H+N+S Landscape Architects
Client: Province of Limburg, Municipality of Venray, Municipality of Horst aan de Maas, Water Board Limburg, Rijkswaterstaat
Design peirod: 2015-2020
Construction time: 2017-2021
Photography: H+N+S Landscape Architects, Siebe Swart, Hans van der Meer, Paul Poels
Awards: Winner of the LILA 2021 in the infrastructure category
版權(quán)聲明:本文版權(quán)歸原作者所有����,請(qǐng)勿以景觀中國(guó)編輯版本轉(zhuǎn)載。如有侵犯您的權(quán)益請(qǐng)及時(shí)聯(lián)系����,我們將第一時(shí)間刪除。
投稿郵箱:info@landscape.cn
項(xiàng)目咨詢:18510568018(微信同號(hào))
 京公海網(wǎng)安備 110108000058號(hào)
京公海網(wǎng)安備 110108000058號(hào)